Persistent or reactivated signaling by the androgen receptor drives the progression of prostate cancer to a deadly form of the disease, namely metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). The RAR-related orphan receptors (RORs) ROR-α, -β, and –γ are nuclear receptors with distinct tissue expression patterns and likely play different physiological functions. The retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γ (RORγ), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, is a ligand-dependent transcriptional factor. In particular, XY018 inhibits RORγ constitutive activity in 293T cells with high potency (EC50, 190 nM).
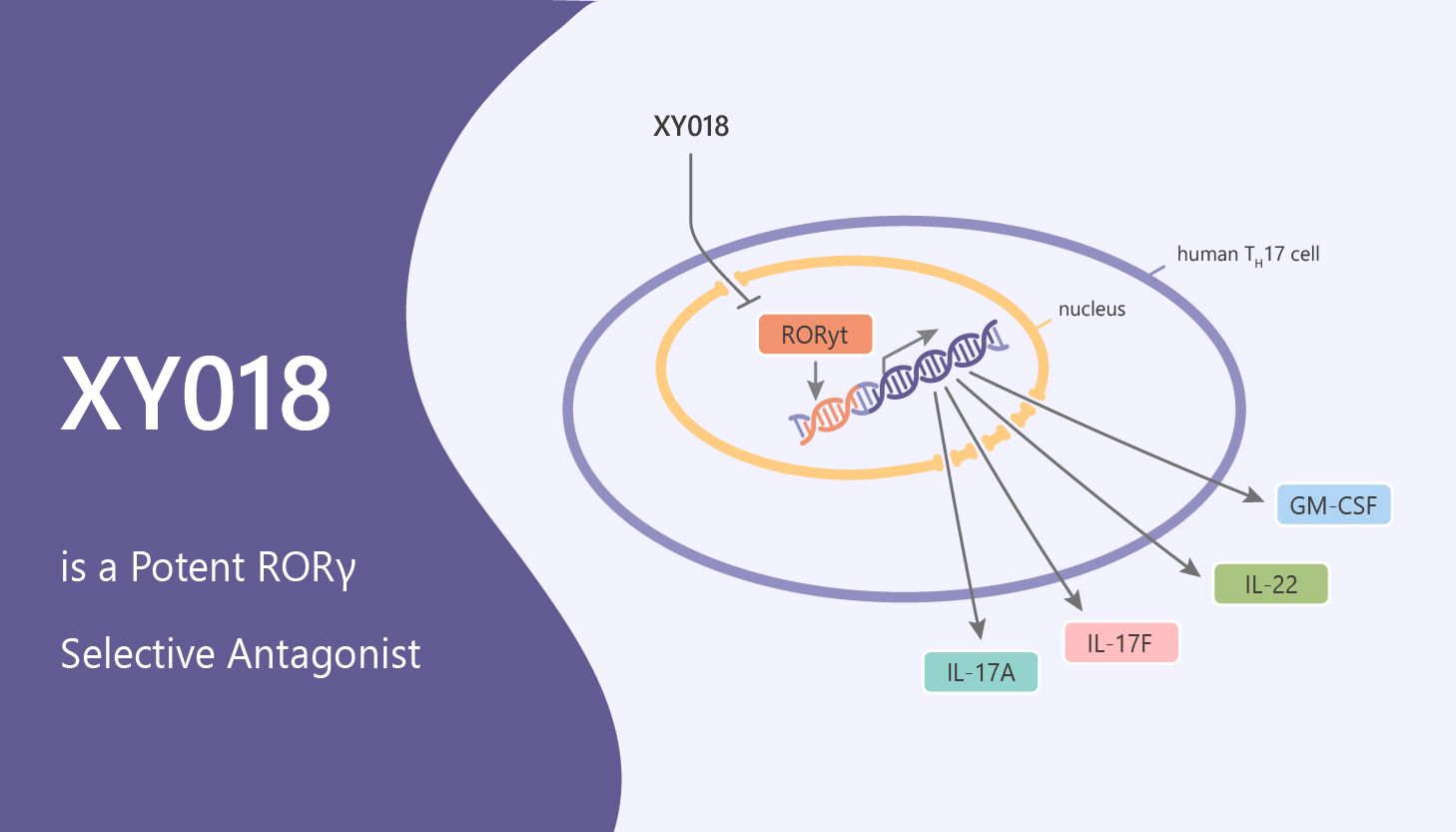
Potent RORγ Selective Antagonist
RORγ functions as a key determinant of androgen receptor overexpression and aberrant signaling in mCRPC tumors. Moreover, RORγ-selective antagonists inhibit AR gene expression, AR genome-wide binding, and growth of mCRPC cell lines in vitro and in mouse xenografts. XY018 binds to the RORγ hydrophobic ligand-binding domain through several conserved hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
In line with the cellular effects, XY018 suppresses the expression of key proliferation and survival proteins, including Myc. The RORγ antagonist (XY018) also inhibits the expression of AR and AR-V7 in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, XY018 displays very weak RORα antagonistic activity (7.57 μM with a maximum of 37% inhibition). Furthermore, XY018 exhibits Kd values in the nanomolar range.
In vivo, XY018 exhibits reasonable pharmacokinetic profiles with a high plasma exposure AUC(0–∞) value of 6444 (μg/L·h) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) value of 839 (μg/L), after a 2 mg/kg iv administration. However, XY018 demonstrates a relatively low oral bioavailability of 19% after an oral administration.
All in all, XY018 is a potent RORγ antagonist for the research of castration-resistant prostate cancer. The potent, selective, metabolically stable, and orally available RORγ antagonists represent a new class of compounds as potential therapeutics against prostate cancer.