Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a member of the insulin receptor superfamily. Specifically, the fusion form can activate ALK, and ALK is continuously activated. Besides, the abnormal activation of ALK abnormally activates its downstream signaling pathway, leading to the occurrence and development of the tumor. Moreover, ALK has always been the treatment target of NSCLC patients. Furthermore, ALK inhibitors have good clinical efficacy in the treatment of NSCLC with advanced ALK rearrangement. Subsequently, there are dozens of other ALK rearrangements or mutations as different carcinogenic forms of ALK across different tumor types. At the same time, the ALK receptor plays a key role in cell communication and normal development and function of the nervous system. Many in vitro functional studies have shown that ALK activation can promote neuronal differentiation in PC12 or neuroblastoma cell lines. ZX-29 is a potent and selective ALK inhibitor and induces apoptosis by inducing ER stress.
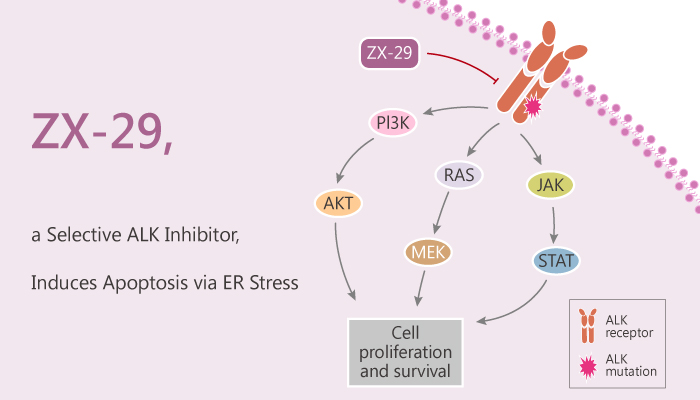
ZX-29 is a potent and selective ALK inhibitor with an IC50 of 2.1 nM, 1.3 nM and 3.9 nM for ALK, ALK L1196M and ALK G1202R mutations, respectively. In addition, ZX-29 is inactive against EGFR. Nonetheless, ZX-29 induces apoptosis by inducing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and overcomes cell resistance caused by an ALK mutation. Meanwhile, ZX-29 also induces protective autophagy and has an antitumor effect. ZX-29 inhibited the survival of NCI-h2228 cells in a time and dose-dependent manner, induced cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase, and then entered cell death. Interestingly, ZX-29 induces protective autophagy, and inhibition of autophagy enhances the antitumor effect of ZX-29. In addition, ZX-29 inhibited tumor growth in a mice xenotransplantation model. All in all, ZX-29 is a potent and selective ALK inhibitor with antitumor activity.
References:
Gou W, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Mar 26;1867(7):118712.