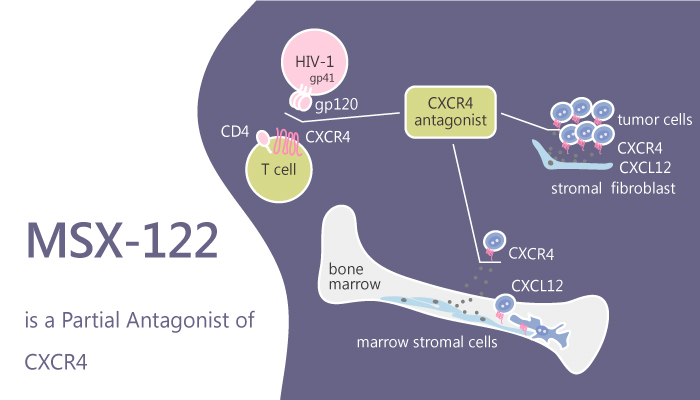
Chemokines and their receptors participate a variety of immune responses to infection, inflammation, and tissue repair. Among them, CXCR4 is a chemokine receptor that has one known natural ligand, CXCL12 also known as SDF-1. Binding of CXCR4 and CXCL12 activates a variety of intracellular signal transduction pathways and effectors that regulate cell survival, proliferation, angiogenesis, chemotaxis, stem cell mobilization, etc. In addition, a study from Michael Natchus in 2008 AACR Annual Meeting firstly reported MSX-122 as an orally available, specific small molecule antagonist of CXCR4/CXCL12.
As we all know, chemokines receptors play a vital role in immune responses. A study from Zhongxing Liang firstly verified the anti-inflammatory properties of MSX-122.
The authors treated the mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) for 7 days, followed by a 3 day recovery with or without MSX-122. As a result, DSS treatment resulted in inflammation manifested by extensive mucosal damage, epithelial erosion, crypt destruction, and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the mucosa and the lamina propria. DSS/MSX-122-treated mice also developed signs of inflammation, but the degree of epithelial erosion and crypt destruction was significantly less. Consequently, MSX-122 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) blocks inflammation induced by carrageenan and lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice.
Moreover, to our excitement, MSX-122 has entered into clinical trials for solid tumor therapy. The anti-tumor anticity of MSX-122 will be introduced next week in “cancer blog”.