The BET (bromodomain and extraterminal domain) family includes BRDT, BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4 epigenetic reader proteins. They contain N-terminal tandem bromodomains, a structural feature that enables the recognition and binding of acetylated lysine residues on histones and other cellular proteins. Thereby, it supports their function as key transcriptional regulators. In addition, they contribute to the pathogenesis of cancer and immune diseases through their effects on transcriptional regulation. BD1 and BD2, structural modules that have attracted great interest as targets for drug development. The BET proteins have become one of the most closely studied protein families in biology. Gilan et al. found that BD1 and BD2 inhibitors altered gene expression in different ways. Moreover, BD2 inhibitors had greater therapeutic activity than BD1 inhibitors in preclinical models of inflammation and autoimmune disease. In this study, GSK046 is a selective and orally active inhibitor of BET with immunomodulatory activity.
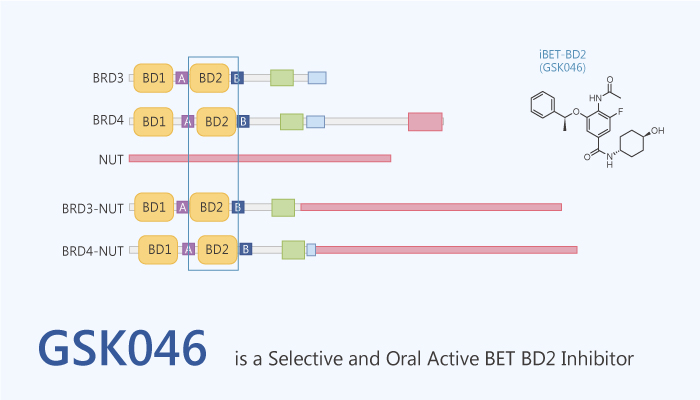
GSK046 is a selective and orally active inhibitor of BET with immunomodulatory activity.
GSK046 is a selective and orally active inhibitor of BET, with the IC50s of 264 nM (BRD2 BD2), 98 nM (BRD3 BD2), 49 nM (BRD4 BD2) and 214 nM (BRDT BD2), respectively. It appears to more prominently affect the recruitment of BRD2 and BRD3 compared to BRD4. Moreover, it reduces the recruitment of BET proteins to interferon (IFN) target genes following IFN-γ stimulation. GSK046 also displays a more selective phenotypic fingerprint, particularly inhibiting the production of key pro-inflammatory mediators including Th17 cytokines in the B and T cell co-culture system. Meanwhile, it does not affect the proliferative activity of human primary CD4+ T cells but still inhibits the production of effector cytokines including IFNγ, IL-17A, and IL-22. Furthermore, it impairs macrophage activation following PMA stimulation, without impacting cellular viability.
In summary, GSK046 is a selective and orally active inhibitor of BET with immunomodulatory activity. And targeting BET proteins in distinct pathologies such as cancer and immunoinflammation is a new strategy.
Reference:
Omer G, et, al. Science. 2020 Apr 24; 368(6489): 387-394.