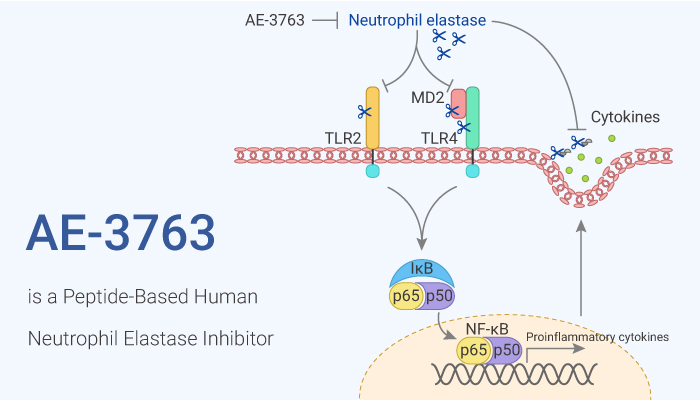
Neutrophil elastase (HNE) is a serine protease, similar to chymotrypsin, and has a wide range of substrate specificity. Specifically, secreted by neutrophils and macrophages during inflammation, it destroys bacteria and host tissue. Besides, HNE may play a role in degenerative and inflammatory diseases through denatured collagen IV and elastin of extracellular matrix. Moreover, HNE is an important protease, which can cause emphysema or emphysema when it is abnormally expressed. HNE has strong catalytic activity and can hydrolyze a variety of extracellular matrix proteins, including elastin. Elastin plays an important role in lung elasticity and proteolytic resistance. Furthermore, HNE can hydrolyze proteins in the body of specialized neutrophil lysozyme and proteins in the extracellular matrix released from activated neutrophils. Meanwhile, HNE plays a role in degenerative and inflammatory diseases through denatured collagen IV and elastin of the extracellular matrix. AE-3763 is a peptide-based human neutrophil elastase inhibitor.
AE-3763 is a peptide-based human neutrophil elastase (HNE) inhibitor
But, how does YUKA1 protect against cancer cells via KDM5A? Let’s discuss it in detail. AE-3763 exhibits potent in vitro inhibitory activity against human neutrophil elastase as well as extremely high solubility and stability in water. Nonetheless, Edema and leukocyte infiltration into the lung are significantly inhibited by infusion of AE-3763. Importantly, AE3763 significantly improves the survival rate by 24 h in a mouse model of fatal shock associated with multiple organ dysfunction. Particularly, AE-3763 dose-dependently prevents hemorrhage when given intravenously by infusion (ED50: 0.42 mg/kg/h) or by bolus injection (1.2 mg/kg). With regard to the toxicity of AE-3763 in mice, the results of a preliminary study have shown no overt toxic effect even at the high dose of 300 mg/kg, iv.
All in all, AE-3763 is a peptide-based human neutrophil elastase inhibitor.
References:
Inoue Y, et al. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Nov 1;17(21):7477-86.