Psoriasis and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), both of them are chronic inflammatory diseases. The characterizes of Psoriasis are mainly red and scaly skin plaques. The topical application of corticosteroid is a common treatment for mild diseases, but they are no longer effective for severe forms. IBD is a chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract and colon.
JAK1 is essential for a wide variety of cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-a, et al. Additionally, JAK3 expression mostly exists in hematopoietic cells and exclusively associates with the γc receptor of type I cytokines. Inactivation mutation or deletion of the JAK3 gene in humans or mice often results in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
In this article, we will introduce a TYK2 inhibitor, GDC-046.
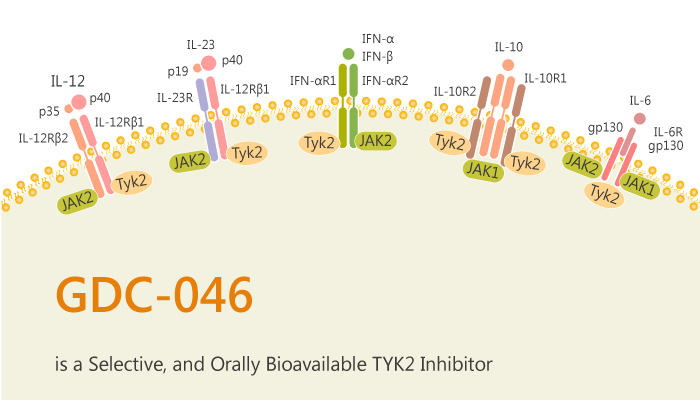
GDC-046 is a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable TYK2 inhibitor with Kis of 4.8, 0.7, 0.7, and 0.4 nM for TYK2, JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3, respectively. In cell-based assays, GDC-046 demonstrates reasonable potency in blocking the IL-12 pathway (IL-12 pSTAT4 EC50=380 nM). At the same time, it also displays less activity in the EPO (JAK2) pathway (EPO pSTAT5 EC50=1700 nM), and IL-6 (JAK1) pathway (IL-6 pSTAT3 EC50=2000 nM).
In vivo, In mice, GDC-046 exhibits relatively high clearance (65 mL/min/kg) when dosed intravenously (i.v. 1 mg/kg) and exhibits modest oral exposure (AUC=2.6 μM·h at p.o. 5 mg/kg).
In mice, when GDC-046 treatment with oral administration at 5 mg/ml, it exhibits Clp, t1/2, Vd and F with 21 mL/min/kg, 1.2 hours, 100 L/kg, and 100%,respectively. Besides, in the rat, it exhibits Clp, t1/2, Vd, and F with 65 mL/min/kg, 0.3 hours, 0.6 L/kg, and 73%, respectively.
Furthermore, Male rats or CD-1 mice are dosed at 1 mg/kg and PO 5 mg/kg as a solution in 60% PEG. It shows statistically significant knockdown of cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ), in a mouse IL-12 PK/PD model.
In conclusion, GDC-046 exhibits acceptable cellular JAK1 and JAK2 selectivity and excellent oral exposure in vivo.
Reference:
Jun Liang, et al. J Med Chem. 2013 Jun 13;56(11):4521-36.