The Tec family kinases include IL-2 inducible T cell kinase (ITK), resting lymphocyte kinase (RLK), Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (Tec), and bone marrow expressed kinase (Bmx). ITK is a tyrosine kinase. It is involves in T cell development, differentiation, and effector function.
ITK, RLK, and Tec are all expressed in T cells. However, ITK and RLK in T cell receptor signaling (TCR), phospholipase γ-1 (PLCγ1) phosphorylation and subsequent Ca2+ mobilization play prominent roles through murine knockout studies. Several groups show that ITK deficiency results in selective impairment of T helper 2 (Th2) cell function relative to other T cell subtypes. Furthermore, following ovalbumin challenge, ITK−/− mice reduces lung inflammation, eosinophil infiltration, and mucous production. The authors use an ITK kinase-dead transgenic mouse model to study. It suggests that ITK kinase activity is required for the control of Th2 responses and the development of allergic asthma.
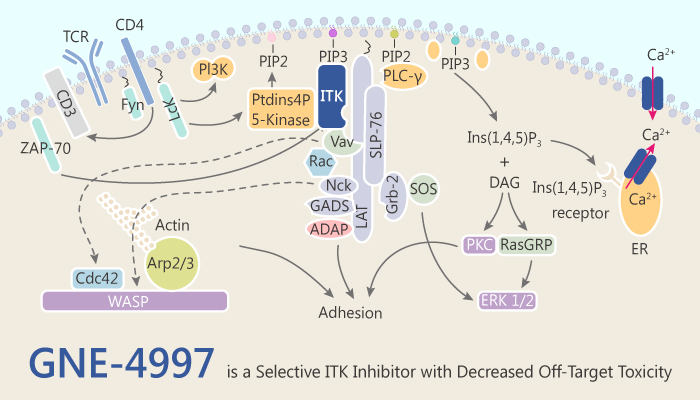
In this study, the authors identify a correlation between the basicity of solubilizing elements in the ITK inhibitors and off-target antiproliferative effects, which can reduce cytotoxicity while maintaining kinase selectivity. GNE-4997 is a potent and selective ITK inhibitor with a Ki of 0.09 nM. Moreover, it obtains that an X-ray crystal structure of GNE-4997 bound to ITK. In addition, GNE-4997 inhibits PLC-γ phosphorylation in Jurkat cells by T-cell receptor stimulation with an IC50 of 4 nM. Furthermore, the correlation between the basicity of solubilizing elements in GNE-4997 and off-target antiproliferative effects reduces cytotoxicity.
In summary, GNE-4997 is a potent and selective interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) inhibitor. It reduces cytotoxicity while maintaining kinase selectivity.
Reference:
Burch JD, et al.J Med Chem. 2015 May 14;58(9):3806-16.