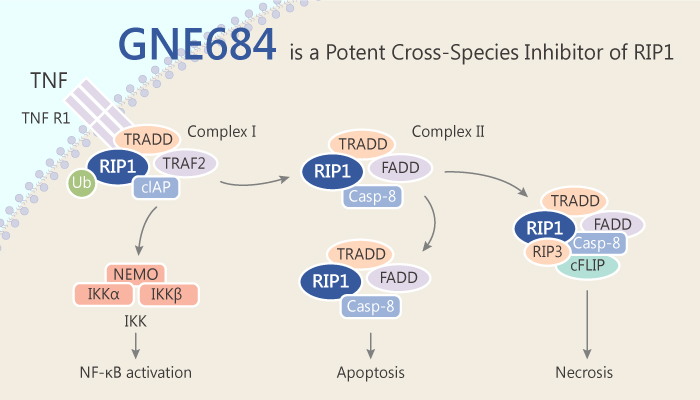
RIP1 is a crucial adaptor kinase on the crossroad of stress-induced signalling pathways and a cell’s decision to live or die. Particularly, RIP1 acts in multiple signaling pathways to regulate inflammatory responses. RIP1 can trigger both apoptosis and necroptosis. Its kinase activity has been implicated in a range of inflammatory, neurodegenerative, and oncogenic diseases. The kinase RIP1, acting downstream of TNFR1 (tumor necrosis factor receptor 1), can trigger apoptosis through binding to FADD, the activating adaptor for caspase-8, or necroptosis through binding to RIP3. RIP1 also contributes to the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling by TNFR1. GNE684 is a potent cross-species inhibitor of RIP1.
In this study, researchers have developed GNE684 as a potent inhibitor of murine RIP1 that is suitable for multi-day dosing.
GNE684 inhibits human RIP1 potently in vitro, and mouse and rat RIP1 with slightly less potency. Accordingly, GNE684 inhibits TNF-induced necroptosis in human HT-29, mouse L929, or rat H9c2 cells. GNE684 also blocks necroptosis in primary human, monkey, and pig colon and stomach, and mouse colon cells, and TB-induced apoptosis in mouse esophagus and small intestine cells. Thus, GNE684 is an efficient inhibitor of RIP1 kinase mediates necroptotic and apoptotic cell death in many species.
Although slightly more potent against human RIP1, GNE684 can also inhibit mouse RIP1 effectively. GNE684 provides much the same level of protection as genetic inactivation of RIP1 in several inflammatory disease models (TNF-driven SIRS, colitis induced by NEMO deficiency in IECs, and collagen antibody-induced arthritis). GNE684 represents an ideal compound for investigating the physiological role of the kinase activity of RIP1 in disease settings.
Collectively, these data identify GNE684 as an effective inhibitor of RIP1 both in vitro and in vivo.