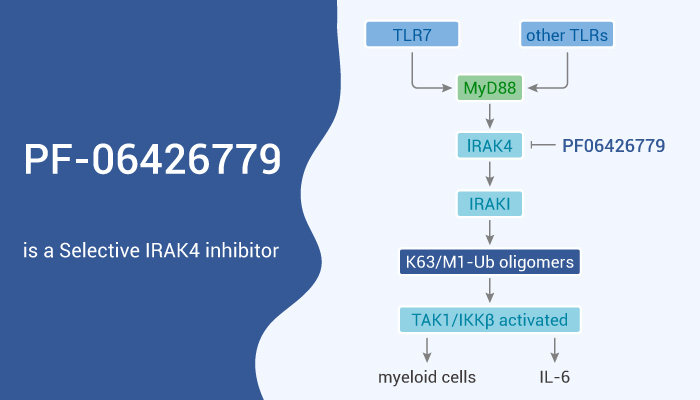
IRAK4 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4) is a protein kinase in the IRAK family. Specifically, IRAK-4 is relevant to signal transduction of innate immune response from toll-like receptors. It also supports signal transduction from T cell receptors. Besides, Compared with IRAK1, IRAK2, and IRAK-M, IRAK4 is unique in that it acts upstream of other IRAs but is more similar to Pelle in this feature. Moreover, IRAK4 is very important for its clinical application. Expressing in T and B lymphocytes, IRAK4 plays an important role in the crosstalk between the innate immune system and adaptive immune system. Furthermore, IRAK4 is important in both kinase-related signaling and stenting. Individuals lacking IRAK4 showed decreased activation of the innate immune response. Meanwhile, selective small molecule inhibitors of IRAK4 may have anti-inflammatory activity and can reduce innate immune response and avoid extensive immunosuppression. PF-06426779 is a potent and selective inhibitor of IRAK4.
PF-06426779 is a potent and selective inhibitor of IRAK4.
But, how does PF-06426779 protect against cancer cells via IRAK4? Let’s discuss it in detail. In the beginning, PF-06426779 is a potent and selective inhibitor of IRAK4 with an IC50 of 0.3 nM. Nonetheless, PF-06426779 inhibits IRAK4, with an IC50 of 12.7 nM in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) assay. Importantly, the active site of IRAK4 has many functions, which makes it a challenging kinase target for drug discovery. Particularly, the most commonly used inhibitors are those with a flat structure and a 4-linked structure. Obviously, when the fluorine substituent was added to the α-site of lactam, PF-06426779 was always more effective than the corresponding defluorination analogs. All in all, PF-06426779 is a potent and selective inhibitor of IRAK4.
References:
Lee KL, et, al. J Med Chem. 2017 Jul 13; 60(13): 5521-5542.