Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) represents a family of inducible transcription factors. The transcription factor NF-κB regulates multiple aspects of innate and adaptive immune functions. NF-κB serves as a pivotal mediator of inflammatory responses. NF-κB induces the expression of various pro-inflammatory genes, including those encoding cytokines and chemokines, and also participates in inflammasome regulation. In addition, NF-κB plays a critical role in regulating the survival, activation and differentiation of innate immune cells and inflammatory T cells.
In this study, researchers evaluated the effects of SP100030 in cultured Jurkat cells and in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Especially, SP-100030 is a potent T cell-specific NF-κB inhibitor. SP100030 inhibits NF-κB activation in vitro as well as suppress the expression of NF-κB-driven genes. Moreover, SP100030 decreases the intensity of both the p50 and p65 supershifted bands.
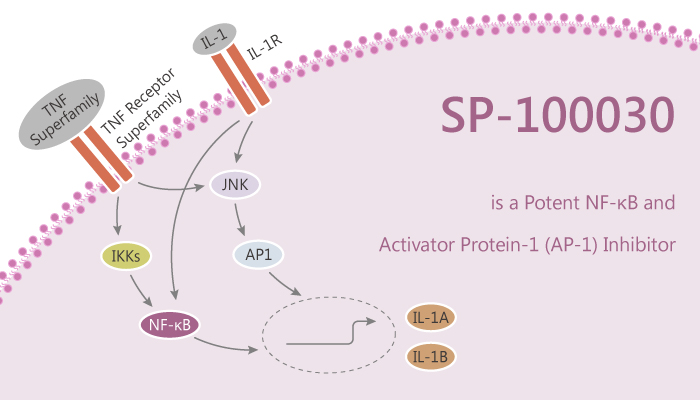
SP100030 inhibits NF-κB-regulated cytokine production at the transcriptional level. Furthermore, SP100030 inhibits cytokine production in a concentration-dependent fashion in Jurkat cells. SP100030 inhibits NF-κB activation in PMA/PHA-activated Jurkat cells by EMSA at a concentration of 1 μM. SP100030 inhibits luciferase production in the Jurkat cells (IC50=30 nM). ELISA and RT-PCR confirm that SP100030 also inhibits IL-2, IL-8, and TNF-α production. Treatment with SP100030 (10 mg/kg/day i.p. beginning on day 21) significantly decreases arthritis severity from the onset of clinical signs to the end of the study.
To summarise, SP100030 behaves as an effective double inhibitor of both NF-κB and AP-1. SP100030 inhibits NF-κB activation in T cells, resulting in reduced NF-κB-regulated gene expression and decreased collagen-induced arthritis. Its selectivity for T cells could provide potent immunosuppression with less toxicity than other NF-κB inhibitors.