The c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) are a series of serine/threonine protein kinases of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. Besides, protein kinases comprise 2% of the mammalian genome and catalyze the transfer of the γ-phosphoryl group of ATP to specific protein substrates. There are three distinct genes encoding JNKs, JNK-1, JNK-2, and JNK-3, and at least 10 different splicing isoforms exist in mammalian cells. Moreover, JNKs bind to substrates and scaffold proteins, such as JIP-1, that contain a D-domain. The three JNK isoforms share more than 90% amino acid sequence identity. Furthermore, the up-regulation of JNK activity is associated with a number of disease states such as type-2 diabetes, obesity, cancer, inflammation, and stroke. Therefore, JNK inhibitors are expected to be effective therapeutic agents against a variety of diseases. SU3327 is a potent, selective and substrate-competitive JNK inhibitor.
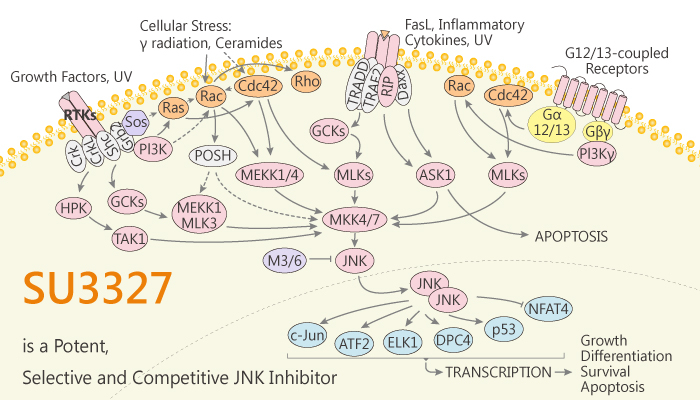
SU3327 is a potent, selective and substrate-competitive JNK inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.7 μM. Specifically, SU3327 also inhibits protein-protein interactions between JNK and JNK Interacting Protein (JIP) with an IC50 of 239 nM. Meanwhile, SU3327 shows less active against p38α and Akt kinase. SU3327 is able to inhibit TNF-α stimulated phosphorylation of c-Jun in the cell (EC50 = 6.23 μM). Nonetheless, SU3327 resulted in a statistically significant reduction in blood glucose levels as compared to vehicle control. In addition, SU3327 treatment possesses the ability to restore insulin sensitivity in mice models of diabetes. Finally, SU3327 has favorable microsomal and plasma stability (T1/2=27 min). All in all, SU3327 is a potent, selective and substrate-competitive JNK inhibitor.
References:
De SK, et al. J Med Chem. 2009 Apr 9;52(7):1943-52.