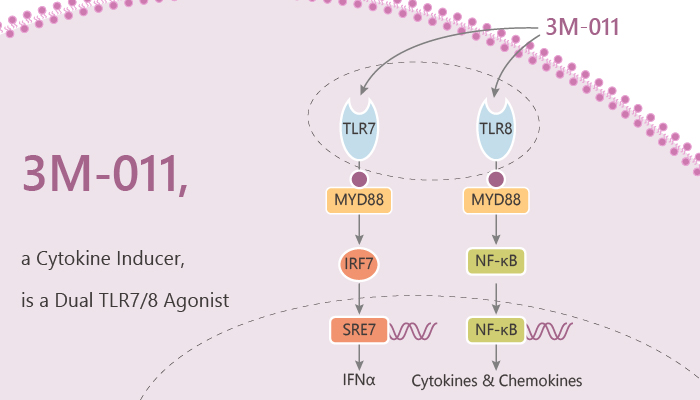
3M-011 is a potent dual toll-like receptor TLR7/8 agonist and a cytokine inducer.
Firstly, in B16-F10 melanoma cells, 3M-011 treatment can decrease B16-F10 melanoma cell counts as a dose-dependent manner. 3M-011 potentiates natural killer (NK) cells cytotoxicity.
The NF-κB reporter stably expresses in HEK-293 cells Then the cells subsequently transiently transfected with human or mouse TLR7 or TLR8. 3M-011 results in a dose-dependent induction of NF-κB-controlled luciferase activity. 3M-011 in humans activates both TLR7 and TLR8, whereas, in mice, 3M-011 activates only TLR7 and not TLR8.
In vivo, in Female SCID/NOD mice with B16-F10 cells. 3M-011 treatment shows antitumor effects in SCID/NOD mice by intravenous injection. In Wild-type C57BL/6 mice, 3M-011 at different doses induce a dose-dependent increase in serum concentrations of both TNF-α and IFN-α/β. Which possesses strongly has antitumor action. Innate immune stimulation with TLR agonists is a proposed modality for immunotherapy of melanoma.
3M-011 is a potent adjuvant to radiotherapy that induces local and profound systemic immune responses during radiotherapy.
Toll-like receptors (TLR) can detect pathogens-expressing molecular patterns. 3M-011 can be a cytokine inducer. In a rat model of human influenza. It is a stand-alone immune response modifier. 3M-011 can significantly inhibit H3N2 influenza viral replication in the nasal cavity after an intranasal (IN) administration.
the ability of the TLR7/8 agonist 3M-011 corrects with Viral inhibition, additionally, some cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-12, and IFN-gamma from rat peripheral blood mononuclear cells also play roles in vivo.
Prophylactic administration of 3M-011 suppresses. influenza viral titers in the lung. When compares to rat recombinant IFN-alpha administration as a high dose, the activity of 3M-011 leads to greater inhibition of viral titers.
In conclusion, 3M-011 significantly inhibits H3N2 influenza viral replication in the nasal cavity. It has the potential for the treatment of respiratory viral infections, such as influenza.
Reference:
Dumitru CD, et al. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Apr;58(4):575-87.