Complement cascade is a key component of the innate immune system and plays a key role in retinal degeneration secondary to Age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Polymorphisms in genes that code for complement or complement regulatory proteins increase the risk of AMD. C5 is a key end-effector component in complement cascade, associated with Stargart macular dystrophy (STGD1). STGD1 is an inherited retinal degeneration that results in loss of central vision. Here’ll describe a specific C5 complement inhibitor, Avacincaptad pegol. It is helpful in retinal cell degeneration therapy, such as STGD1 and geographic atrophy (GA).
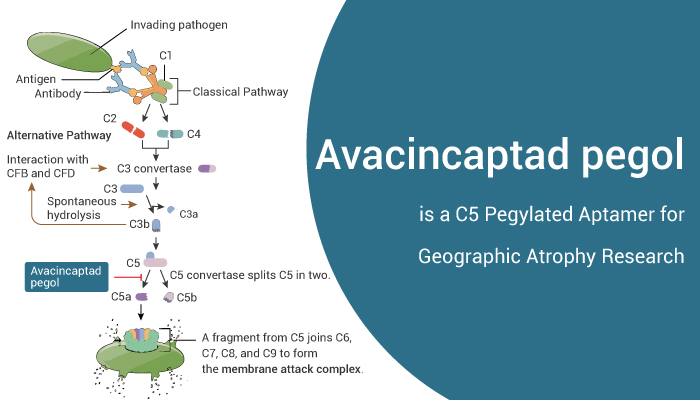
Avacincaptad pegol is a pegylated RNA ligand that is a specific C5 complement inhibitor.
When immune lesion activates the complement cascade, producing the complement C3 convertase to cleave complement C3 and resulting in the subsequent production of the complement C5 convertase, which cleaves complement C5 into C5a and C5b. C5a fragments may activate inflammasomes that lead to pyroptosis and cell death, and C5b may be involved in the formation of the membrane attack complex (C5B-9), which ultimately leads to cell death. Avacincaptad pegol can inhibit C5 cleavage and avoid cell degeneration caused by C5 lysate.
In in vivo experiments, Avacincaptad pegol is generally well tolerated. There are no adverse events or inflammation. Administered by intravitreal injection, it significantly reduces the growth of GA in the eye in AMD cases. Avacincaptad pegol may slow down retinal cell degeneration and inhibit GA. Importantly, STGD1 treatment is designed to reduce toxic diretinoic acid and lipofercin in the retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Avacincaptad pegol can effectively reduce inflammation-related RPE damage and has a protective effect on the retina.
In summary, Avacincaptad pegol is an effective C5 complement inhibitor, which can effectively inhibit GA lesions and STGD1 in AMD, and has a protective effect on retinal cell degeneration.
References:
[1] Rehan M Hussain, et al. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 Oct;18(10):1049-1059.
[2] Glenn J Jaffe, et al. Ophthalmology. 2021 Apr;128(4):576-586.