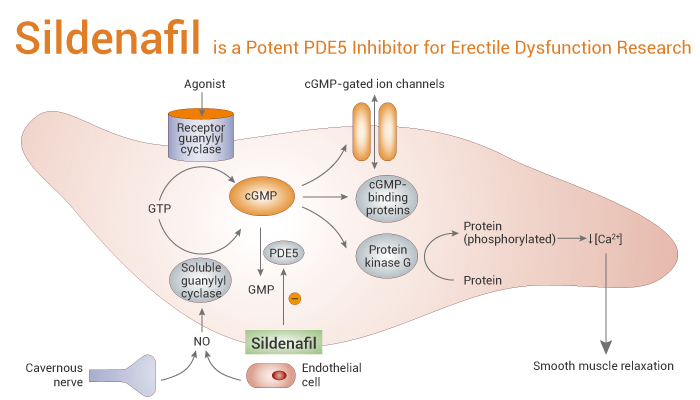
Sildenafil (UK-92480), the first selective type 5 phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitor, was developed less than 20 years ago. Initially, it was considered as a potential anti-angina drug. It later evolved into an on-demand oral medication for erectile dysfunction, known as Viagra. More recently, it has become a new orally active treatment for pulmonary hypertension, called Revatio. In preclinical studies, Sildenafil displayed vasodilatory effects, abrogated platelet aggregation. And it inhibited thrombus reformation in a damaged carotid artery.
Sildenafil is a potent PDE5 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 5.22 nM.
First, Pretreatment with Sildenafil (UK-92480) (1 μM) potentiates the phosphorylation of ERK1/ERK2. It also increases the percentage of cells in S phase and cell proliferation. Secondly, Pretreatment with Sildenafil (1 μM) citrate followed by serotonin stimulation leads to dramatic increase in OD value to 0.33. Besides, Sildenafil (1 μM) obviously enhances the upregulation of ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation induced by serotonin.
In the dog model of erection, Sildenafil citrate significantly increases ICP and ICP/BP but shows no significant effect on BP compared with vehicle. Meanwhile, Sildenafil (10 mg/kg) significantly decreases the number of TL+-cells. Finally, Sildenafil citrate has been reported to decrease flap necrosis in preclinical animal models by increasing the secretion of growth factors (FGF and VEGF). And it histologically is shown to be effective in rat cavernous nerve architecture.
Reference:
[1] Ghofrani HA, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Aug;5(8):689-702.
[2] Li BB, et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011 Sep;124(17):2733-40.