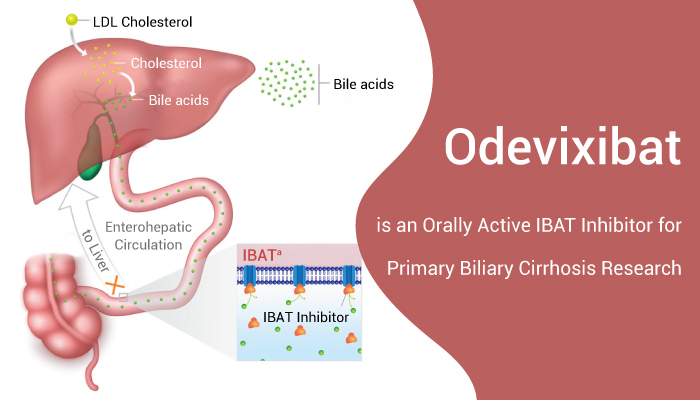
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a rare chronic cholestatic liver disease. In addition, the characteristics of PSC are inflammatory destruction of the intrahepatic and/or extrahepatic bile ducts, leading to bile stasis, fibrosis, and ultimately to cirrhosis, and often requires liver transplantation (LT). When symptomatic, the most common presenting symptoms are abdominal pain, pruritus, jaundice or fatigue. Moreover, PSC occurs more commonly in men, and is typically diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 40. Besides, most cases occur in association with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which often precedes the development of PSC. According to the most recent epidemiological studies, PSC affecting around 0.006-0.016% of the population. Of these, around 75% have concomitant IBD. However, PSC can be complicated by bacterial cholangitis, dominant strictures (DSs), gallbladder polyps and adenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) and, in patients with IBD, colorectal malignancy. Terriblely, PSC is a progressive disease, yet no effective medical therapy for halting disease progression has been identified. Hence, we will introduce, Odevixibat (A4250), a apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) inhibitor, which can be used in PSC research.
Odevixibat is a selective and orally active ASBT inhibitor for PSC research.
In vivo, Odevixibat (0.01% (w/w) in chow diet; 4 weeks) improves sclerosing cholangitis and significantly reduces serum alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase and BAs levels, hepatic expression of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic genes and bile duct proliferation in Mdr2-/- mice.
Importantly A4250 significantly reduced biliary BA secretion but preserved HCO3– and biliary phospholipid secretion resulting in an increased HCO3–/BA and PL/BA ratio.
All in all, Odevixibat is a novel, highly potent ASBT inhibitor, reduces bile toxicity by decreasing biliary BA output and concentration, resulting in an improvement of sclerosing cholangitis in Mdr2-/- mice. In other words, Odevixibat is a promising agent for PSC research.
Reference:
[1] Baghdasaryan A, et al. J Hepatol. 2016 Mar;64(3):674-81.
[2] Da Cunha T, et al. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022 Jun 28;10(3):531-542.
[3] Rabiee A, et al. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Apr 5;6:29.