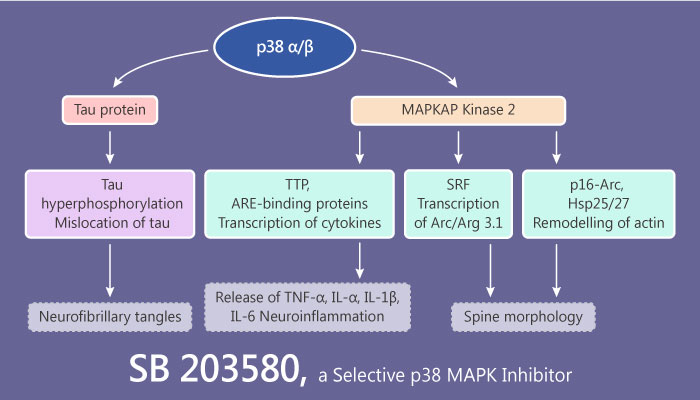
SB 203580 was identified as a selective p38 MAPK (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases) inhibitor over 20 years ago. And it shows more than 100-fold selectivity over Akt (PKB), LCK, and GSK-3β. There have a large numbers of articles published reported the function of SB 203580 in regulating the production of inflammatory cytokines.
A study from K.J. Escott described the effect of SB 203580 on allergic airway in-flammation in the animal models.
Firstly, the authors got Female Brown Norway rats (180-200 g) and allowed free access to food and water. The rats were sensitized on days 0, 12 and 21 with ovalbumin (100 mg) administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) with aluminium hydroxide (100 mg) in saline (1 ml). And SB 203580 was administrated with the dose of 10-100 mg/kg orally 30 min prior to ovalbumin challenge. The compound was also administered orally 30 min before and 4 h after challenge with the same dosage.
As a result, there was a significant increase in BAL TNF-a 1 h after aerosolized ovalbumin challenge and SB 203580 significantly (P<0.05) inhibited BAL TNF-a levels at all of the doses tested (10-100 mg/kg). However, oral administration of SB 203580 (10-100 mg/kg) had no significant effect on airway eosinophilia in comparison to the vehicle treated, challenged group. Surprisingly, SB 203580 produced a dose-related increase in lung tissue monocyte/macrophage cell numbers. In other words, SB 203580 inhibited systemic
TNF-a production induced by LPS and also displayed anti- arthritic activity in both rats and mice.
During the last 20 years, the scientists studied the compound again and again, however, there has no clinical trials reported. Further work need to be carried out and we are looking forward.