Cartilage is a smooth elastic tissue, covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints. Articular cartilage is a kind of cartilage, acts based on the extracellular matrix (ECM). The latter one consists of proteoglycan and collagens. Articular cartilage has a very limited repair capabilities. Once cartilage damage happens, the chondrocytes are unable to migrate to the damaged area. They are bound in lacunae. Unfortunately, joint surface injuries often induce osteoarthritis. Thus, it is necessary to find out more agents for repairing cartilage.
Glycoprotein 130 (gp130) belongs to the IL-6 receptor family. It mediates chronic, low-grade inflammation established by articular cartilage injury. The latter finally causes osteoarthritis. Therefore, modulator of gp130 has the potential in cartilage repair.
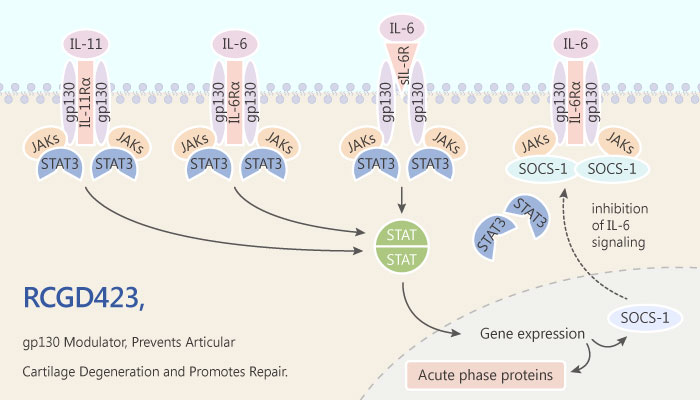
In recent study, researchers discovered a potent compound as a gp130 modulator, RCGD423. It directly modulates gp130 by enhancing homodimerisation.
Firstly, RCGD423 is a hypertrophy inhibitor. It exerts decrease in RUNX2 and COL 10 protein levels in osteoarthritic articular chondrocytes.
As a result, in adult articular chondrocytes, the modulator stimulates the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis.
Moreover, in vivo, RCGD423 stops articular cartilage degeneration. Besides, the animals receiving 4 µg RCGD423 showed no obvious cartilage degradation. However, control animals exhibited significant cartilage loss.
In addition, RCGD423 enhances cartilage repair in rats. After receiving the modulator, animals dramatically improved cartilage resurfacing.
RCGD423 is a potent gp130 modulator, prevents cartilage degradation, and increases cartilage repair. Researchers need to do more to find out the potential in cartilage loss therapy.
References:
1. Shkhyan R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 May;77(5):760-769.