Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the lungs. It is a common disease due to genetic and environmental factors. However, there is no cure for this disease. We can prevent symptoms through avoiding triggers. Allergens and irritants are usual triggers. Thus, we need to find out more agents to treat asthma.
P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38 MAPK) are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases. They involve in cellular process, such as cell differentiation, apoptosis and autophagy. P38 MAPK respond to stress stimuli, including heat shock, ultraviolet irradiation and inflammatory cytokines. Inhibition of p38 MAPK plays an important role in autoimmune diseases and inflammatory processes.
Underwood DC, et al carried out a study, they found a potent p38 MAPK inhibitor SB 239063 as an anti-asthma agent.
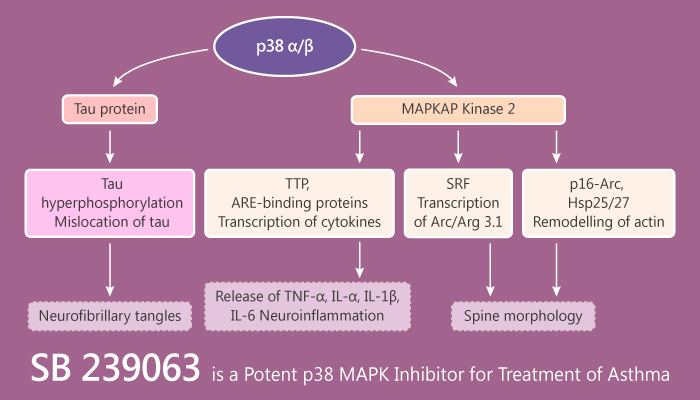
On one hand, SB 239063 potently and selectively inhibits p38 MAPK. SB 239063 exhibits an IC50 of 44 nM for recombinant purified human p38α. SB 239063 shows equipotent inhibitory activity against p38α and p38β. But it has no effect on p38γ or p38δ. Moreover, SB 239063 does not alter other kinases related to MAPK.
Furthermore, SB 239063 selectively inhibits IL-1 and TNF-α production in LPS-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes.
On the other hand, SB 239063 (12 mg/kg) dramatically suppresses antigen-induced airway eosinophilia in mice via oral administration. In addition, the inhibitor also exhibits similar activity in guinea pigs.
Taken together, SB 239063 is a potent, selective and orally active p38 MAPK inhibitor. It has the potential in the treatment of asthma and other inflammatory disorders.
References:
1. Underwood DC, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Apr;293(1):281-8.