Menin is a protein encoded by the MEN1 gene. MLL fusion proteins interact directly with menin to regulate the expression of MEIS1 and HOX genes, which drive leukemogenesis in MLL leukemia. Consequently, targeting the menin-MLL protein-protein interaction using small-molecule inhibitors is a promising therapeutic strategy for MLL leukemia. Besides, chromosomal translocations characterize MLL leukemia at 11q23 and the expression of MLL fusion proteins. Specifically, it has a very poor prognosis and is resistant to current therapies. Moreover, preclinical data show that extended drug exposure is required for menin inhibitors to achieve anti-leukemia activity in vitro. Furthermore, several classes of peptidomimetic compounds and nonpeptide small-molecule menin inhibitors have been reported. To date, all published menin inhibitors are reversible in nature. Irreversible menin inhibitors may have much greater anti-leukemia activity and efficacy than reversible menin inhibitors. M-525 is a first-in-class, highly potent, irreversible and covalent menin-MLL protein-protein interaction inhibitor.
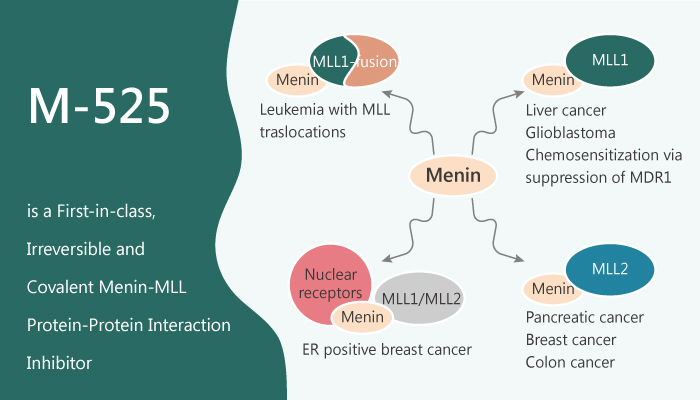
M-525 is a first-in-class, highly potent, irreversible and covalent menin-MLL protein-protein interaction inhibitor with anti-leukemia activity. In addition, M-525 binds to menin with an IC50of 3 nM and achieves low nanomolar potencies in cell growth inhibition and in the suppression of MLL regulated gene expression in MLL leukemia cells. Meanwhile, It demonstrates the high cellular specificity over non-MLL leukemia cells and is >30-times more potent than the corresponding reversible inhibitors. Importantly, A single administration of M-525 effectively suppresses MLL-regulated gene expression in tumor tissue. M-525 achieves an IC50 of 3 nM in the MV4;11 cell lines and has an IC50 of 2 µM in the HL-60 cell line. All in all, M-525 is a first-in-class, highly potent, irreversible and covalent menin-MLL protein-protein interaction inhibitor with anti-leukemia activity.
References:
Xu s, et al. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Feb 5;57(6):1601-1605.