Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of Zn2+-binding, Ca2+-dependent endopeptidases. They play a prominent role in the physiological and pathological degradation of mammalian extracellular matrix (ECM).
The activity of MMPs can be controlled at different levels: gene expression, proteolytic activation, inhibition by endogenous inhibitors and proteolytic feedback loops.
MMPs structure includes a signal peptide, a propeptide domain, a catalytic domain (HexxHxxGxxH), and a haemopexin-like domain that links to the catalytic domain by a hinge region.
Because of the substrate specificity, amino acid similarity, and identifiable sequence module. MMPs have at least distinct subclasses: collagenases, gelatinases, stromelysins, matrilysin, MT-MMPs, and metalloelastase (MMP-12).
MMP-12 possesses certain distinct biological and biochemical processes. MMP-12 plays an important role in the migration of monocytes/macrophages through the basement membrane. Moreover, MMP-12 is an inhibitor of angiogenesis that could reduce tumor progression and some other inflammatory diseases.
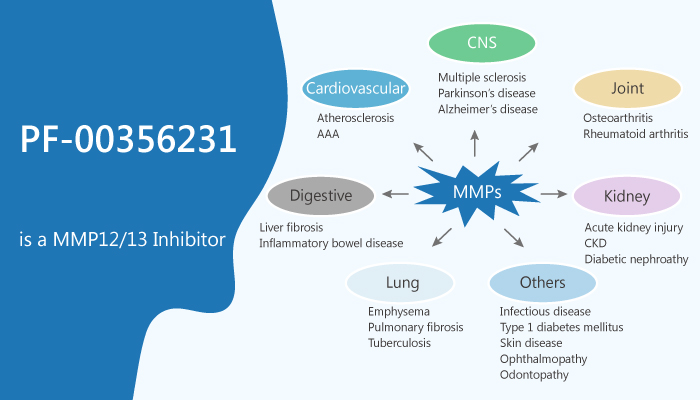
It is urgent to find an MMP12 inhibitor. In this article, we will introduce a novel non-peptidic, non-zinc chelating MMP12/13 inhibitor, PF-00356231.
In the crystal structures of MMP-12/PF-00356231, the asymmetric unit (AU) is composed of a dimer. The two protein molecules pack together with their catalytic clefts. As a result, the inhibitor actually forms a part of the dimer interface. PF-00356231 binds to MMP-12 and forms the PF-00356231/MMP-12 complex. It shows potency against MMP-12 and MMP-13 with IC50S of 1.4 μM and 0.65 nM, respectively. In the structures of MMP-12/PF-00356231, the RMS difference between monomers A and B in its AU is 0.27 Å.
Because of the amino acid sequence variability, the size and shape of the S1′ pocket vary in different MMP members. MMP-1 and MMP-7 have small and closed S1′ pockets. However, MMP-12 has a larger and more hydrophobic pocket. this pocket is part of a channel running through the protein, opening onto the far side of the protein surface.
PD-0359601 stabilizes itself by a greater number of hydrogen bonds and by numerous hydrophobic interactions with amino acids lining the S1’pocket. The structures of the complexes with inhibitor PF-00356231 reveal that its central morpholinone and thiophene ring locates the inhibitors halfway down the S1′ pocket.
In summary, PD-0359601 is a specific, non-peptidic, non-zinc chelating ligand and inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-12. Meanwhile, it central morpholinone and thiophene rings sit over the Zn atom at a distance of approximately 5A, locating the inhibitors halfway down the S1′ pocket.
Reference
Morales R, et al. J Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 20;341(4):1063-76.