Multiple myelomas (MM) is a plasma cell malignancy that accounts for approximately 10% of all hematological malignancies. Many new drugs and therapies apply to this disease, but it remains an incurable hematological disorder. The characterizes of MM contain the excess clonal proliferation of abnormal plasma cells, over-secretion of monoclonal proteins in the serum or urine, and various organ damage, such as renal failure, hypercalcemia, anemia, and lytic bone resorption.
The serine/threonine kinase Traf2- and NCK-interacting kinase (TNIK) belongs to the ger; minal center kinase (GCK) family. These regulatory kinases play an important role in cell spreading or migration through the cytoskeleton organization. TNIK has been a popular target in several types of cancers during the decade. And many published-articles prove that the expression of TNIK involves the survival of human cancer cells, for example colorectal, gastric, liver, and hematological cancer.
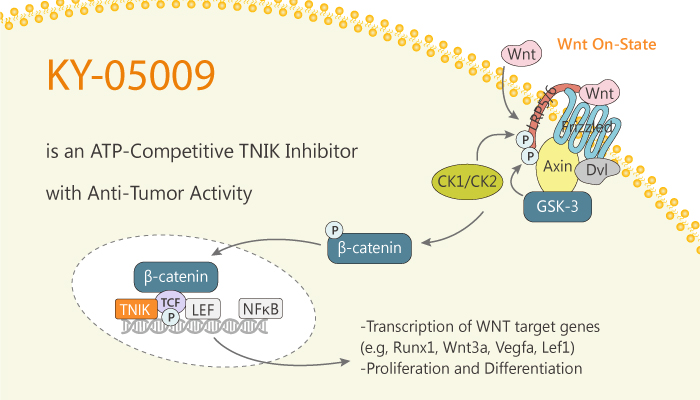
TNIK interacts with β-catenin and the following process is the phosphorylation of T-cell factor (TCF)4. Then the p-TCF4 activates the Wnt signaling.
In this article, we will introduce an ATP-competitive TNIK inhibitor, KY-05009.
Firstly, in RPMI8226 cells, KY-05009 inhibits the proliferation of cells in a dose-dependent manner. Besides, KY-05009 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in RPMI8226 cells as a concentration-dependent manner. Nextly, when KY-05009 treatment for 1 hour, this compound suppresses the transcriptional activity of Wnt signaling-related genes.
Lastly, to confirm the synergistic inhibitory effect of KY-05009 and dovitinib on IL-6-induced activation of Wnt signaling in MM cells.
KY-05009 applies in cell alone or combines with dovitinib in IL-6-induced MM cells for 24 or 48 h. IL-6 alone increases the cell proliferation rate, however, KY-05009, dovitinib, and the combination group affects cell viability. Notably, this phenomenon also exists in other multiple myeloma cell lines such as IM-9 and MM.1R cells.
Besides, KY-05009 or Dovitinib inhibits the IL-6-induced TCF4-mediated transcription at 3 μM, and combination application significantly supressesTCF4-mediated transcriptional activity at the same dose. IL-6 alone elevates TNIK, CTNNB1, TCF7, and TCF4 mRNA expression, but KY-05009 reserves their expression. Above all, We can find that KY-05009 contributes to the IL-6-induced proliferation of MM cells through the inhibition of TNIK-mediated Wnt signaling.
In conclusion, KY-05009 is a novel aminothiazole TNIK inhibitor, exhibits anti-cancer activity in MM cells. The suppression of TNIK and Wnt signaling by KY-05009 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of Wnt signaling-activated cancer cells.
Reference:
Lee Y, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):41091-41101.