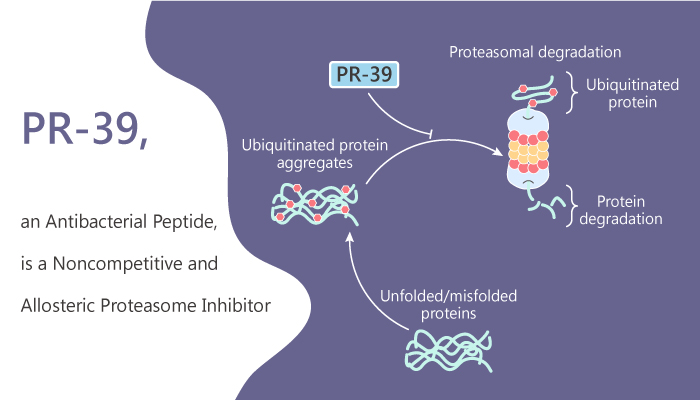
Degradation of proteins in mammalian cells via two distinct pathways: lysosome-dependent and proteasome-dependent. PR-39 is a proline- and arginine-rich antibacterial peptide. It is also a noncompetitive, reversible, and allosteric proteasome inhibitor. PR-39 reversibly binds to the α7 subunit of the proteasome and blocks degradation of NF-κB inhibitor IκBα by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, PR-39 blocks TNF-α-induced activation of VCAM-1. Additionally, it also inhibits IκBα degradation without significantly affecting overall protein degradation in cells. Alternatively, PR-39 may interfere with another, yet unknown, step involved in IκBα degradation by the proteasome.
PR-39 alters the shape of the 20S and 26S cylinder and affects the binding of 19S caps in a reversible manner.
It specifically blocks the degradation of IκBα and HIF-1α by the proteasome. The 26S proteasome catalyzes the hydrolysis of proteins by conjugation to ubiquitin. 20S proteasome is the core of the 26S proteasome, which has four stacked rings.
Finally, PR-39 binds to the α7 subunit alters the three-dimensional proteasome architecture or interaction of the 20S particle and the 19S regulatory subunit. As a result, this will affect the entry of certain protein substrates into the 20S cylinder. All of those results show that PR-39 inhibition of IκBα degradation is dose-dependent and reversible.
In an acute myocardial infarction mice model, the αMHC-PR39 mice express PR-39 peptide selectively in cardiac myocytes. Additionally, PR-39 shows a significantly small infarct in mice compares to the saline group in mice. stimulates angiogenesis, inhibits inflammatory responses and significantly reduces myocardial infarct size in mice.
Besides, in an acute injury mice model, caerulein induces acute pancreatitis. Pretreatment with PR-39 blocks IκBα degradation and NF-κB-dependent transcription in the mouse pancreas after induction of acute pancreatitis.
In conclusion, The peptide PR-39 represents an allosteric inhibitor that forms the basis for precise manipulations of proteasome function.
Reference:
[1]. Maria Gaczynska, et al. Biochemistry. 2003 Jul 29;42(29):8663-70.
[2]. Y Gao, et al. J Clin Invest. 2000 Aug;106(3):439-48.