Innate immunity is the first-line cellular stress response. Additionally, it is a good way for defending the host cell against invading pathogens. These processes involve pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) through sensing by diverse pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Following, the subsequent activation of cytokine and type I interferon gene expression are also triggered.
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) acts as the predominant sensor for aberrant double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). This originates from pathogens or mislocalization or misprocessing of cellular dsDNA
Binding of dsDNA to cGAS can active the synthesis of c[G(2′,5′)pA(3′,5′)p]. As a result, This protein can activate the endoplasmic reticulum membrane-anchored adaptor protein, a stimulator of interferon genes. Activated-STING recruits and activates TANK-binding kinase 1. In turn, it phosphorylates the transcription factor family of interferon regulatory factors (IRFs).
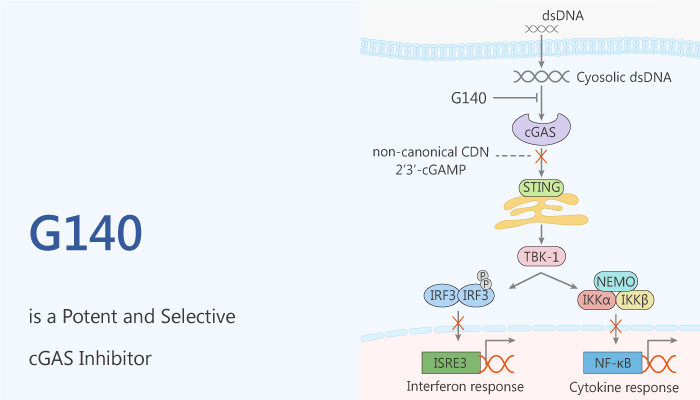
cGAS pathway plays an important way in the host defense against invading pathogens, cellular stress, and genetic factors. However, the cGAS pathway may also cause the production of aberrant cellular dsDNA. For example, Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS) is a lupus-like severe autoinflammatory immune-mediated disorder due to loss-of-function mutations in TREX1.
In previous, RU.521 is a potent inhibitor of blocking m-cGAS (IC50=0.11 µM) as well as in mouse macrophages (IC50=0.70 µM) without interfering with other innate immunity pathways.
In this article, we will introduce a potent cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) inhibitor, G140.
In a human THP1 cell, G140 inhibits h-cGAS in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 1.70 µM. Besides, in the primary macrophages cells, G140 inhibits h-cGAS in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 0.86 µM.
This inhibitor also has inhibitory effects on h-cGAS and m-cGAS, exhibits IC50 values of 14.0 nM and 442 nM, respectively. In THP1 cells, G140 inhibits cell viability with an LD50 of >100 µM.
In conclusion, G140 is a potent inhibitor with h-cGAS to further the understanding of cGAS function in humans. It paves the way for the development of cGAS inhibitor against some autoimmune diseases.
Reference:
Lama L, et, al. Nat Commun. 2019 May 21; 10(1): 2261.