Guanylate cyclase (guanylyl cyclase, GC), which catalyzes the formation of cGMP from GTP, exists in both the soluble and particulate fractions of cells. The GC family consists of particulate GC (pGC) and a nitric oxide-activated soluble GC (sGC). Among them, cGMP generated by sGC is an important second messenger. In addition, sGC regulates activity of several enzymes triggering such important physiologic reactions as vasodilation, smooth muscle relaxation and platelet aggregation. Furthermore, the NO-sGC-cGMP axis belongs to the key signal transduction pathways involved in regulating the cardiovascular system. sGC displays a high affinity for, and is activated by, the first messenger signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO). This binding leads to the stimulation of sGC, resulting in increased production of intracellular second messenger cGMP.
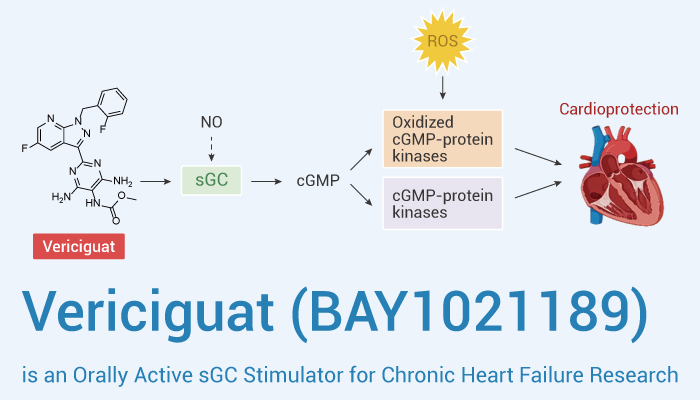
Vericiguat (also known as BAY1021189) is a potent, selective and orally active soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator.
Vericiguat has the potential for chronic heart failure research. This compound inhibits phenylephrine-induced contractions of rabbit saphenous artery rings, rabbit aortic rings, and canine femoral vein rings. In addition, Vericiguat inhibits the U46619-induced contractions of porcine coronary artery rings concentration dependently. Moreover, Vericiguat predominantly acts on the heme-containing nonoxidized form of sGC. Besides, in rat heart Langendorff preparations, ex vivo, Vericiguat reduces the coronary perfusion pressure in a concentration-dependent manner.
Finally, Vericiguat exhibits good pharmacokinetic profile by far, with a low clearance and long half-life in rats and dogs after intravenous dosing, as well as high oral bioavailability. In addition, Vericiguat has no inhibitory effects on major CYP isoforms (1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4). Importantly, Vericiguat can maintain heart and kidney function in a model of hypertension-induced end-organ damage, with substantially reduced overall mortality.
In summary, Vericiguat is a potent, selective and orally active sGC stimulator for chronic heart failure research.
References:
[1] Markus Follmann, et al. J Med Chem. 2017 Jun 22;60(12):5146-5161.