DPP4 belongs to the dipeptidyl peptidases family. DPP4 is a serine protease detected on several immune cells and on epithelial cells of various organs. Besides the membrane-bound enzyme, a catalytically active soluble form is present in several body fluids. Moreover, DPP4 plays a key role in immune-regulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, cell adhesion, and apoptosis by targeting different substrates. Therefore, DPP4 inhibitors are commonly potential hypoglycemic agents. As reported, Sitagliptin is an orally active inhibitor of DPP4 with an IC50 of 19 nM. Meanwhile, Sitagliptin increases the incretin levels, and prolongs insulin secretion in animal models. Thus, Sitagliptin can be used for type 2 diabetes mellitus research. Sitagliptin has been approved by FDA in 2006.
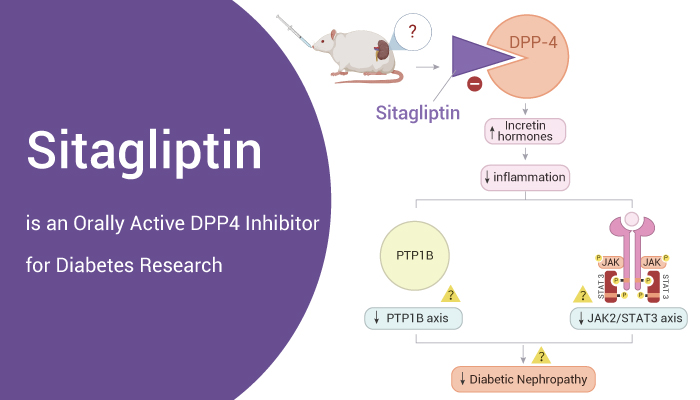
Sitagliptin, a DPP4 Inhibitor, is a hypoglycemic agent for diabetes research.
In vitro, Sitagliptin (0.1-2 μM, 2 h) significantly increases total GLP-1 secretion in intestinal L cells. Meanwhile, Sitagliptin also stimulates cAMP synthesis and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in L cells. Besides, Sitagliptin (100 nM, 6 h) decreases DPP-4 activity in bovine retinal endothelial cell (EC), and prevents retinal EC dysfunction triggered by the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α.
In vivo, Sitagliptin (100 mg/kg; oral gavage) reverses hyperglycemia and weight loss and alleviates diabetic nephropathy in Streptozotocin (30 mg/kg; i.p.) induced diabetic rats. In addition, Sitagliptin alleviates Streptozotocin-induced alterations in inflammatory biomarkers, such as IL-6 and TNF-α. Sitagliptin also reduces P-JAK2, P-STAT3, and PTP1B proten level in the kidney. Furthermore, Sitagliptin (4 g/kg in diet, for 1 month before surgery) improves islet graft survival in nonobese diabetic mice, an autoimmune type 1 diabetes model.
To sum up, Sitagliptin is an orally active DPP4 inhibitor. Sitagliptin shows potent hypoglycemic effect in diabetic animal models.
References:
[1] Al-Qabbaa SM, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 31;24(7):6532.
[2] Kim SJ, et al. Diabetes. 2009 Mar;58(3):641-51.
[3] Sangle GV, et al. Endocrinology. 2012 Feb;153(2):564-73.
[4] Gonçalves A, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jun;102:833-838.