CXC chemokine receptors are the complete membrane proteins and they can specifically bind and respond to CXC chemokine family cytokines. Specifically, they represent a subfamily of chemokine receptors, a large family of G protein-linked receptors. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a G protein-coupled receptor, which is initially associated with leukocyte trafficking and HIV infection. Besides, CXCR4 is expressed in a variety of tumors including GBM. Moreover, high level of CXCR4 expression is usually of prognostic significance CXCR4 is a chemokine receptor of seven transmembrane domain (7TMR) 4. Furthermore, CXCR4 is relevant to stem cell homing to bone marrow, cancer biology and metastasis, and HIV infection. The function of the chemokine receptor subset is as co-receptor for HIV-1 entry. CXC chemokine receptor CXCR4 and CC chemokine receptor CCR5 are the main co-receptors for T cell line entry. TC14012 is a selective and peptidomimetic CXCR4 antagonist and CXCR7 agonist.
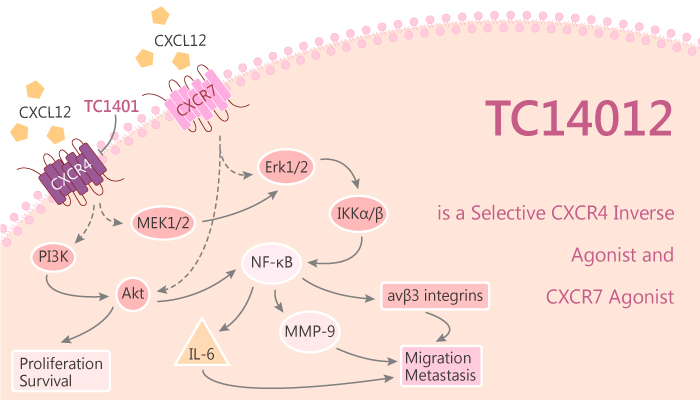
TC14012 is a selective and peptidomimetic CXCR4 inverse agonist and CXCR7 agonist.
How does TC14012 work on the targets? Let’s study it together. In the beginning, TC14012 is a selective and peptidomimetic CXCR4 antagonist with an IC50 of 19.3 nM. Furthermore, TC14012 is a potent CXCR7 agonist with an EC50 of 350 nM for recruiting β-arrestin 2 to CXCR7. TC14012, a serum-stable derivative of T140, has anti-HIV activity and anti-cancer activity.
In addition, TC14012 inhibits more than 95% ofthe infection of the CXCR4-expressing cells by the HXB2 (X4) or 89.6 (dual-tropic) strain with 1 mM. Nonetheless, TC14012 does not inhibit all the infection of the CCR5-expressing cells by the SF162 (R5) or 89.6 (dual tropic) strain with 1 mM. Nonetheless, TC14012 leads to erk 1/2 phosphorylation in U373 cells, which express endogenous CXCR7 but not CXCR4. Upon stimulation with TC14012, CXCR7 and the CXCR7-Cter4 chimera are able to recruit arrestin, whereas CXCR4 and CXCR4-Cter7 remain silent.
All in all, TC14012 is a selective and peptidomimetic CXCR4 inverse agonist and CXCR7 agonist.
References:
Stéphanie Gravel, et al. J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 3;285(49):37939-43.