Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a kind of lung disease. The symptoms are obvious, including shortness of breath and cough with sputum production. It always worsens over time.
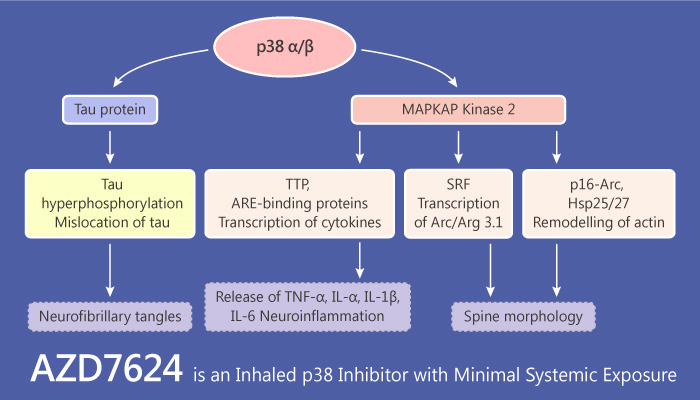
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is an important protein. It regulates and activates key pro-inflammatory mediators. p38 exhibits high levels in patients with COPD. Moreover, the degree of lung disease is much related to activation of p38.
Therefore, inhibition of p38 becomes a hot target, and inhaled inhibitors are more convenient.
AZD7624 is a potent p38 inhibitor via inhaled delivery. It exhibits potent activity in the following assays.
To begin with, human alveolar macrophages produce increased TNFα in the presence of LPS. AZD7624 suppresses the increase partially, with a pIC50 of 9.0. Similar effects exist in human PBMC and whole blood, AZD7624 has pIC50 values of 8.4 and 8.1, respectively.
Besides, AZD7624 exhibits excellent activity in ex vivo assay. It blocks LPS-induced increase in TNFα with a pIC50 of 8.2.
Furthermore, AZD7624 displays potent bioavailability after inhalation. In rats, oral administration of the inhibitor exhibits low bioavailability. Consequently, researchers chose intravenous and inhalation administration. As a result, the dose-adjusted lung AUC after inhalation is five times higher than after intravenous administration.
In conclusion, AZD7624 is a potent p38 inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity. The compound inhibits LPS-induced TNF-α. It also exhibits good pharmacokinetic property after inhalation.
References:
1. Pehrson R, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Jun;365(3):567-572.