Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are type I membrane glycoproteins. They contain intracellular Toll–IL-1 receptor homology (TIR) domains. TLRs recognize a wide range of ligands including lipopolysaccharide, double-stranded RNA and lipoprotein. TLRs differ in their expression among different cell types. Their signal-transduction pathways also vary, being dependent on either myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) or TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β, on the basis of adaptor usage. TLR8 recognizes viral or bacterial single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and activates innate immune systems. In addition, the hepatitis B virus (HBV) infects more than 300 million people worldwide and is a common cause of liver disease and liver cancer. HBV is a small DNA virus with unusual features similar to retroviruses. Selgantolimod is an orally active and selectiveTLR8 agonist for the treatment of the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
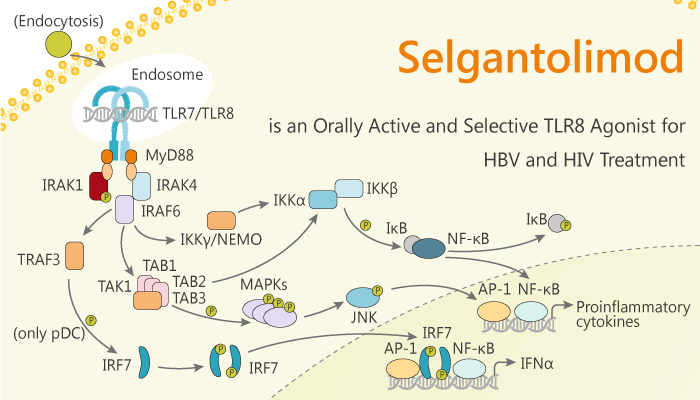
Selgantolimod induces the cellular immune mediators’ interleukin (IL) -12 and IL-8, as well as the antiviral cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ (IFNγ) in vitro in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Moreover, it activates natural killer (NK) and mucosal-associated invariant T cells. Meanwhile, Selgantolimod stimulates a cluster of differentiation (CD)-8+ T-cell proliferation and increases IFNγ production. Selgantolimod lowers programmed cell death protein 1 expression by HBV-specific CD8+-T cells in vitro in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Selgantolimod-induced cytokines reduce HBV DNA, RNA, and antigen levels in HBV-infected primary human hepatocytes. Once-weekly dosing of oral Selgantolimod induces dose-dependent increases in serum IL-12 and IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) in cynomolgus monkeys. Selgantolimod also leads to a functional cure in the woodchuck model of chronic HBV.
In summary, Selgantolimod is a potent, orally active, and selective TLR8 agonist for the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
Reference:
Jules Levin. Multicenter Study. 2019 Nov 8-12.