Osteoarthritis (OA) is a major global health burden. Osteoarthritis becomes an increasingly greater threat to human well-being at present. P2Y receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) for extracellular nucleotides. There are eight mammalian P2Y receptor subtypes (P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y4, P2Y6, P2Y11, P2Y12, P2Y13, and P2Y14). The primary human osteoarthritis chondrocytes show significantly higher expression of P2Y11R at both the mRNA and protein levels.
P2X3 and P2X2/3R play an important role in the development of articular hyperalgesia of arthritic joints. Targeting the P2X7R may be a potential treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). P2Y11 receptor is an immune-regulatory receptor. The P2Y11 receptor is a member of the purinergic receptor family. In addition, P2Y11R plays a role in TNF-α-induced degradation of type II collagen. NF157 ameliorates TNF-α-induced degradation of type II collagen.
NF157 is a highly selective nanomolar P2Y11 antagonist with a pKi of 7.35. The IC50s are 463 nM, 1811 µM, 170 µM for P2Y11 (Ki=44.3 nM), P2Y1 (Ki=187 µM), P2Y2 (Ki=28.9 µM), respectively. In particular, NF157 is the first nanomolar P2Y11 antagonist with a pKi of 7.35. Moreover, NF157 displays selectivity for P2Y11 over P2Y1 (650-fold), P2Y2 (650-fold), P2X2 (3-fold), P2X3 (8-fold), P2X4 (22-fold), and P2X7 (67-fold) but no selectivity over P2X1. NF157 may be helpful for studies evaluating the physiological role of P2Y11 receptors. P2Y11R may be a suitable target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Furthermore, NF157 displays potent at P2Y11 receptor with a Ki of 44.3 nM. P2Y11 receptors carrying the mutation have reduced Ca2+ and cAMP signaling properties.
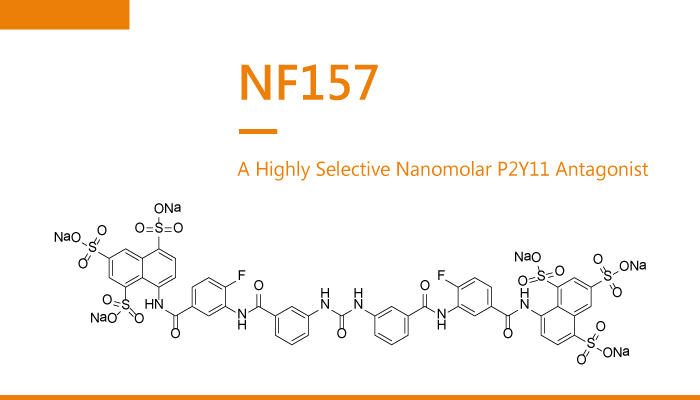
All in all, NF157 is the first nanomolar P2Y11 antagonist for the treatment of osteoarthritis.