Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a receptor for IL-12R and belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family, subfamily 4. This cytokine acts as a growth factor for activated T and NK cells. And it enhances the lysate activity of natural killer cells or lymphokine-activated killer cells. Morever, it stimulates IFN-γ production through resting PBMC. Il-12β (IL-12B) is the main functional chain of IL-12. It can heterodimerize with IL-12 p35 subunit (IL-12A) to form IL-12, or with IL-23 p19 subunit (IL23A) to form IL-23. In terms of signal transduction, IL-12 signaling is mediated by p-STAT4.
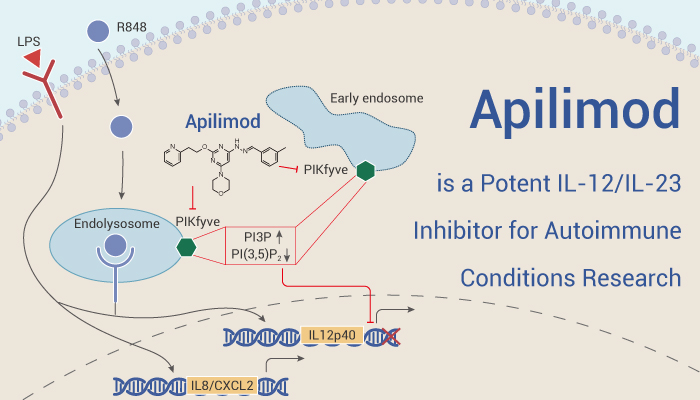
Apilimod is a Potent IL-12/IL-23 Inhibitor for Autoimmune Conditions Research
Apilimod (STA 5326) is a potent IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor. And it strongly inhibits IL-12 with IC50s of 1 nM and 2 nM, in IFN-γ/SAC-stimulated human PBMCs and SAC-treated monkey PBMCs, respectively. And it is also a potent and highly selective PIKfyve inhibitor.
In Vitro, Apilimod inhibits IFN-γ production induced by either IFN-γ/SAC or SAC in human PBMCs, with an IC50 value of approximately 20 nM. Apilimod inhibits IFN-γ/SAC-induced TNF-α and ConA-induced IL-5 from human PBMCs at high concentrations. But it shows no inhibition against IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, and IL-18 in all cultures tested. Apilimod (100 nM) completely inhibits IFN-γ/LPS or IFN-γ/SAC-induced p35 and p40 promoter-driven luciferase activity.
In Vivo, Apilimod (10 mg/kg, p.o.) is effective not only when administered throughout the entire experiment, but also when administration is initiated on day 30 when disease is clearly measurable but not maximal. TA-5326 causes a significant reduction in cell number only in the Th1 model, with an average percentage of inhibition of 51%±8% relative to the vehicle control. Apilimod treatment has no effect in the Th2 setting. Apilimod (5 or 20 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces the level of IL-12 p40 in serum without altering body weight in EAU mice. Oral administration of Apilimod reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) by clinical and histopathological analysis.
In conclusion, Apilimod is a potent IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor for autoimmune conditions research.
Reference:
[1] Blood. 2007 Feb 1;109(3):1156-64.
[2] Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(5):R122.