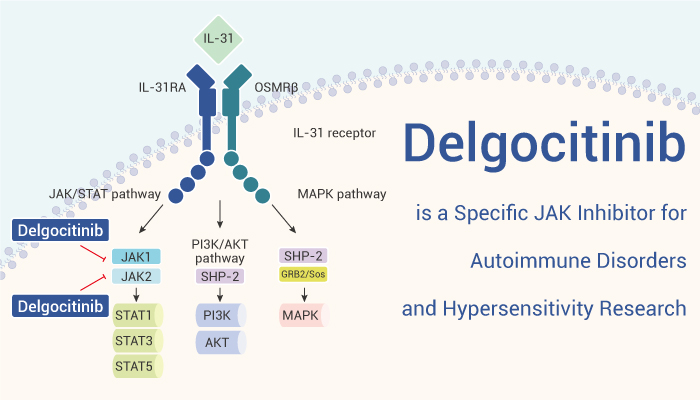
The Janus kinase (JAK) family of nonreceptor protein-tyrosine kinases consists of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2 (Tyrosine Kinase 2). In addition, the family of cytokines that bind type I and type II cytokine receptors, including interleukins (ILs), interferons (IFNs), and colony-stimulating factors, as well as classic hormones such as erythropoietin, prolactin, and growth hormone, are important for acquired, innate immunity and hematopoiesis. Signaling via these receptors is dependent on a small family of structurally distinct kinases named the Janus kinases (JAKs). However, JAK1/3 signaling participates in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders while JAK1/2 signaling contributes to the development of myeloproliferative neoplasms as well as several malignancies including leukemias and lymphomas. Hence, we will introduce a specific JAK inhibitor-Delgocitinib (JTE-052).
Delgocitinib is a specific and orally active JAK inhibitor for autoimmune disorders and hypersensitivity research.
In vitro, Delgocitinib (0-1000 nM) inhibits JAK activity in an ATP-competitive manner on JAK enzymes, with IC50 values of 2.8, 2.6, 13, and 58 nM for JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and Tyk2, respectively. In addition, Delgocitinib inhibits the phosphorylation of Stat proteins induced by IL-2, IL-6, IL-23, GM-CSF, and IFN-α with IC50 values of 40, 33, 84, 304, and 18 nM, respectively. Moreover, Delgocitinib inhibits IL-2-induced proliferation of T cells in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 value of 8.9 nM.
Delgocitinib not only shows good anti -inflammation activities in vitro, but also in vivo.
Delgocitinib (0.1-10 mg/kg; p.o.; single) at 1 or 6 h prior to the IL-2 injection can decrease the IFN-γ production (inhibits the inflammatory response) in DBA/1J mice.
In a word, Delgocitinib is a promising JAK inhibitor for research of inflammation and immunity.
Reference:
[1] Tanimoto A, et al. Inflamm Res. 2015 Jan;64(1):41-51.
[2] Roskoski R Jr. Pharmacol Res. 2022 Sep;183:106362.