Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic muscle disease. And The feature is contraction-induced myofibre injury and inflammation. Besides, researchers found that NF-κB signaling is active in dystrophin deficient muscle. Therefore, Inhibiting NF-κB is a potent strategy for the treatment of DMD. Vamorolone (VBP15) is an orally active steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. It’s a GR ligand, and also a MR antagonist. Furthermore, Vamorolone shows potent NF-κB inhibition effect, and improves muscular dystrophy without side effects.
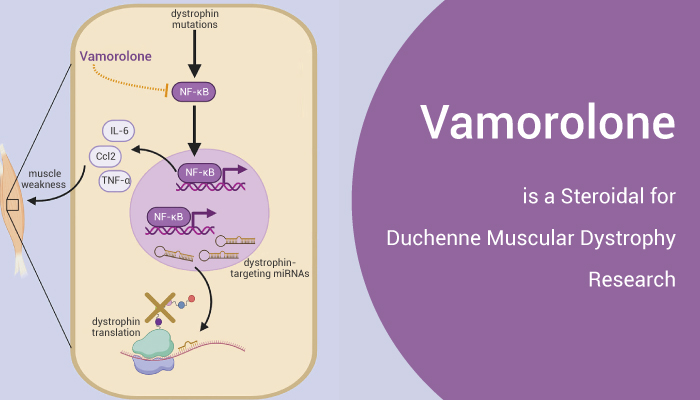
Vamorolone, orally active steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, is potent against duchenne muscular dystrophy.
In vitro, Vamorolone (10 nM-10 μM) inhibits TNFα-induced NF-κB signaling in NF-κB reporter assays in C2C12 muscle cells, and also inhibits inflammatory transcripts Cox2, Irf1 and Nos2 expression (p < 0.005). In laser injury and dye exclusion assays, Vamorolone (1-100 μM) reduces impact of the injury and enhances repair. Besides, Vamorolone (10 μM) shows anti-inflammatory effects in muscle, immune and heart cells, determined by the inhibition on Irf1, Mcp1, Il1b, and Il6 induction.
In vivo, Vamorolone (30 mg/kg; p.o.; daily for 20 days) reduces CNS inflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis male outbred CD-1 mice. Specifically, Vamorolone reduces inflammatory foci by 75 %, and reduces several proinflammatory mediators such as Cxcr4, Il16, Ccl6, Vcam1, etc. Vamorolone (5-30 mg/kg; in cherry syrup) shows a protective effect in mdx mice, including improved MR-mediated hypertension and mdx cardiomyopathy phenotypes.
In conclusion, Vamorolone is orally active steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. It’s a GR ligand, a MR antagonist, and also a NF-κB activation inhibitor. Vamorolone can protect against membrane damage. And it also improves muscular dystrophy and reduces inflammation in DMD model mice.
References:
[1] Heier CR, et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Oct;5(10):1569-85.
[2] Dillingham BC, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;35(3):377-387.
[3] Heier CR, et al. Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Feb 11;2(1). pii: e201800186.