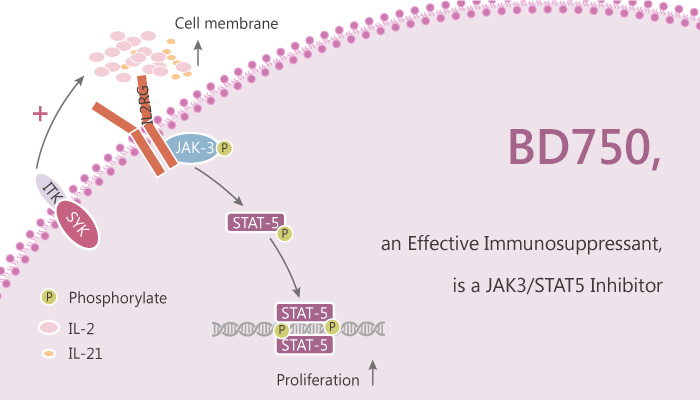
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a pleiotropic cytokine and controls the differentiation and homeostasis of both pro- and anti-inflammatory T cells. The IL-2 receptor couples to JAK tyrosine kinases and activates the STAT5 transcription factors. BD750 inhibits T cell proliferation by affecting the JAK3/STAT5 signalling pathway. Especially, BD750 is an effective immunosuppressant.
Anti-CD3/anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies or an alloantigen stimulate T cell proliferation. BD750 significantly inhibits mouse and human T cell proliferation with IC50 values of 1.1±0.2 μM and 1.3±0.2 μM respectively. In particular, BD750 inhibits T-cell proliferation without obvious cytotoxicity in vitro. Furthermore, BD750 induces cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1phase in activated T cells. In IL-2-stimulated CTLL-2 cells and primary activated T cells, BD750 inhibits cell proliferation and STAT5 phosphorylation, but not Akt or p70S6K phosphorylation. Moreover, BD750 also reduces hypersensitivity response in mice in a dose-dependent manner.
BD750 inhibits IL-2-induced JAK3/STAT5-dependent T cell proliferation. BD750 has the potential to be a lead compound for the design and development of new immunosuppressants for preventing graft rejection and treating autoimmune diseases. Treatment with increased concentrations (0.625, 2.5, and 10 μM) of BD750 increases the percentages of T cells at the G0/G1 phase. BD750 inhibits cell proliferation and STAT5 phosphorylation in IL-2-stimulated CTLL-2 cells and primary activated T cells. Treatment with BD750 induces tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDC). The tolDC inhibits pro-inflammatory T cell immunity in vitro and in vivo.
In summary, BD750 is a safe and effective inhibitor of T cell-mediated inflammation in vivo. Potentially, BD750 acts as a lead compound for the design and development of new immunosuppressants for the prevention of graft rejection and autoimmune diseases.