Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is a key node in innate inflammatory signaling. It is also directly downstream of the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) family of receptors. Besides, IRAK4 expresses in T or B lymphocytes and plays a critical role in cross-talk between the innate and adaptive immune systems.
Selective small-molecule inhibitors of IRAK4 has anti-inflammatory activity. At the same time, it attenuates the innate immune response while avoiding broad immunosuppression. The main characteristic of chronic autoimmune diseases is the aberrant activation of the innate immune system.
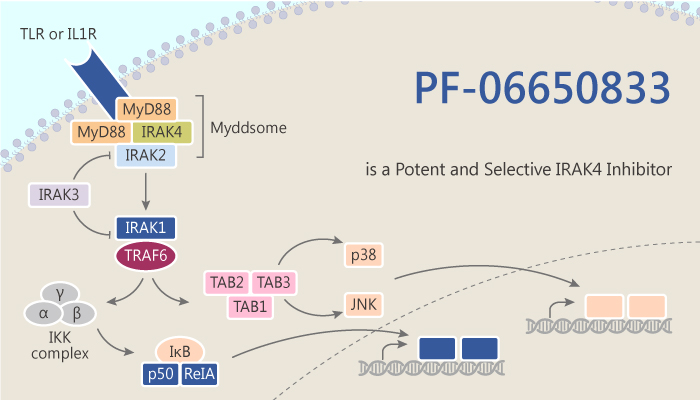
In this article, we will introduce a potent IRAK4 inhibitor, PF-06650833.
The kinome selectivity profile of PF-06650833 is assessed in a panel of 278 kinases (Invitrogen) at 200 nM inhibitor concentration using the ATP Km for each kinase. PF-06650833 leads to an approximately 100% inhibition for IRAK4.
In a whole-cell functional VEGF2R assay, Lactam PF-06650833 exhibits no activity is observed at concentrations up to and including 30 μM. Additionally, in a voltage clamp assay, PF-06650833 inhibits hERG current by 25% at 100 μM.
In pooled human liver microsomes and probe substrates for the CYP450 enzymes, PF-06650833 at 3 μM exhibits a less than 5% inhibition of CYPs 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2D6, and 3A4. Lactam PF-06650833 shows a time-dependent inhibitory effect on six major CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, and 2D6).
Besides, when using cryopreserved human hepatocytes, PF-06650833 exhibits a potential induction of CYP3A and affords a 4.4-fold increase in mRNA at 10 μM.
Lastly, in vivo, in Male Sprague-Dawley rats, At 2.5 hours after oral administration of PF-06650833 at 0.3, 1, 3, and 30 mg/kg. The mean exposures of PF-06650833 in plasma are 2.1 nM, 7.7 nM, 19 nM, and 150 nM free, respectively. Furthermore, PF-06650833 treatment significantly inhibits LPS-induced TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner.
In conclusion, PF-06650833 acts as a potent, selective, and orally active inhibitor of IRAK4. It has the potential for rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and lymphomas research.
Reference:
Lee KL, et al. J Med Chem. 2017 Jul 13;60(13):5521-5542.