Interleukin 10 (IL-10) is an anti-inflammatory cytokine. Specifically, IL-10 is a cytokine with multiple effects in immune regulation and inflammation. Besides, it downregulated Th1 cytokines, class II MHC antigens, and costimulatory molecules on macrophages. Anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 promotes immune homeostasis through a variety of mechanisms, including inhibiting inflammatory cytokines produced by innate immune cells and promoting Treg function. Moreover, small molecular probes provide important insights into the regulation of IL-10 in innate immune cells. Therefore, increasing the abundance of signal transduction of IL-10 may be a feasible treatment strategy for the recovery and maintenance of immune homeostasis. Furthermore, CDK8 and cyclin C are associated with complex mediators and regulate transcription through several mechanisms. Meanwhile, CDK8 binds and/or phosphorylates a variety of transcription factors, which may activate or inhibit the function of transcription factors. BRD6989 inhibits CDK8 and upregulates IL-10.
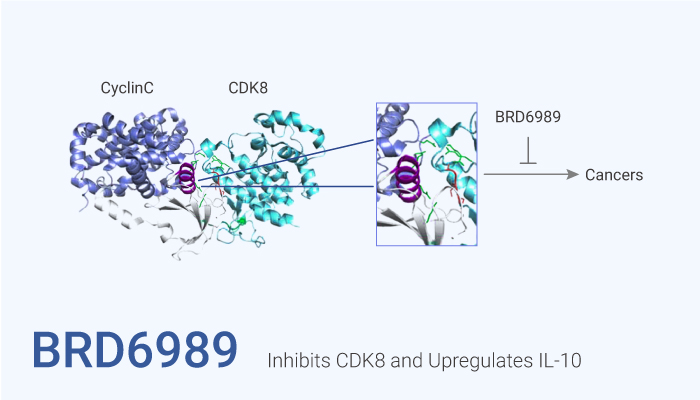
BRD6989 inhibits CDK8 and upregulates IL-10.
How does BRD698 work on the target? Let’s study it together. In the beginning, BRD6989, an analog of the natural product cortistatin A (dCA), inhibits CDK8 and upregulates IL-10. Nonetheless, BRD6989 selectively binds a complex of CDK8 with an IC50 of ~200 nM. Nonetheless, BRD6989 inhibits the kinase activity of recombinant CDK8 or CDK19 complexes.
In the second place, BRD6989 with 0-100 μM for 48 hours increases IL-10 production with an EC50 of ~1 μM in BMDCs. Particularly, BRD6989 with 0.6-15 μM suppresses phosphorylation of the STAT1 transactivation domain at Ser727 in IFNγ-stimulated BMDCs. Obviously, BRD6989 suppresses the induction of STAT1-STAT2 activity and NF-κB activation to a varying degree after stimulation of BMDMs. Additionally, BRD6989 enhances IL-10 production in activated human and murine macrophages and dendritic cells.
All in all, BRD6989 inhibits CDK8 and upregulates IL-10.
References:
Johannessen L, et al. Nat Chem Biol. 2017 Oct;13(10):1102-1108