NF-κB is a transcription factor with heterodimer or homodimer form of rel family proteins such as RelA (p65), RelB, cRel, p50 and p52. NF-κB binds to inhibitory κB (IκB) proteins such as IκBα, IκBβ, IκBε, p105 and p100. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a major component of the outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS can trigger a variety of inflammatory reactions by binding to Toll-like receptor 4. Activation of IKK complex results in phosphorylation of IκB, which marks for ubiquitination followed by proteasome-mediated degradation. IκB degradation unmasks the nuclear localization signal of NF-κB, allowing the transcription factor to translocate to the nucleus. NF-κB binds to the promoter region of immune and inflammatory genes for transcriptional regulation. JSH-23 is a specific inhibitor of NF-κB nuclear translocation.
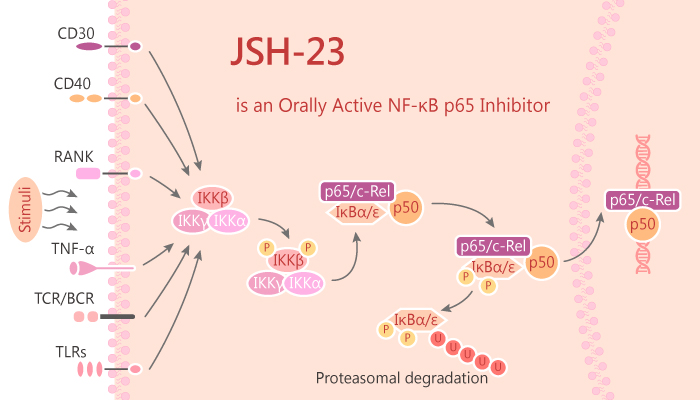
In this study, JSH-23 exhibits inhibitory effect with an IC50 value of 7.1 μM on NF-κB transcriptional activity in LPS-stimulated macrophages RAW 264.7. Moreover, JSH-23 rescues Ang II-driven IL-1β production in ATG5siRNA-treated cells and decreases the proportion of cells in G2/M phase. Besides, JSH-23 interferes LPS-induced nuclear translocation of NF-κB without affecting IκB degradation. JSH-23 treatment significantly reverses the nerve conduction and nerve blood flow deficits seen in diabetic animals. NF-κB inhibition by JSH-23 shows decreased superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) expression and SOD activity together with increased conjugated dienes (CD) concentration in the heart of hereditary hypertriglyceridemic (HTG) rats. NF-κB inhibition by JSH-23 leads to increase blood pressure in the model of hereditary hyperglyceridemic rats.
All in all, NF‐κB binds to the promoter region of immune and inflammatory genes for transcriptional regulation. JSH-23 is a specific inhibitor of NF-κB nuclear translocation.