Liver fibrosis is the accumulation of connective tissue in the liver. The consequence results from an imbalance between production and degradation of the extracellular matrix. Because inflammation histologically presents in virtually all forms of liver fibrosis, several anti-inflammatory strategies have been tested to efficiently prevent hepatic fibrogenesis. COX-2, a key executor of uncontrolled inflammation, is an inducible immediate-early gene originally identified to be up-regulated by several proinflammatory stimuli, including cytokines, mitogens, and growth factors. In addition, COX-2 always relates to progressive hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C infection. In fact, selective COX-2 inhibitors are effective in the prevention of fibrotic disorders. Today, I’d like to introduce an orally active COX-2 specific inhibitor SC-236. Additionally, SC-236 is also a PPARγ agonist.
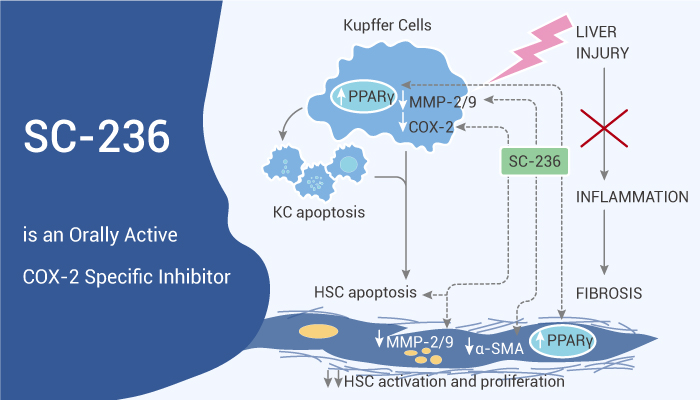
Firstly in vitro, SC-236 (15 μM, 30 min) suppresses the side effects of NSAIDs and prevented inflammation in vECs subjected to ALSS. At the same time, it significantly induces PPARγ expression in HSCs and acted as a potent PPARγ agonist in a luciferase-reporter trans-activation assay.
Secondly, SC-236 strongly inhibits, in a time- and concentration-dependent manner, macrophage viability. In addition, SC-236, either alone or in combination with 15d-PGJ2, induced a marked pro-apoptotic effect in HSCs in culture.
In vivo, SC-236 (6 mg/kg, gavage) exhibits anti-fibrotic properties in CCl4- treated animals. The researchers also detected marked induction of COX-2 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in the liver of CCl4-treated rats. Moreover, SC-236 significantly reduced the degree of liver fibrosis. It also dramatically suppressed α-SMA expression in CCl4-treated rats.
In total, SC-236 suppresses activator protein-1 (AP-1) through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. SC-236 exerts anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing phosphorylation of ERK in a murine model
Shao-Yu Fang, et al. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020 Sep 9.