The retinoic acid X receptor (RXR) is a core member of the nuclear receptor protein family. Acts as a ligand-regulated transcription factor. RXR, the heterodimeric partner of VDR, is a 55 kDa protein that binds 9-cis retinoic acid as its ligand. Besides, it exists in cells and tissues, including those that do not express VDR. Retinoid X receptors RXRα, β, and γ (NR2B1, NR2B2, and NR2B3), members of the nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily of ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators, bind DNA response elements associated with target genes. Importantly, RXR plays a role in many physiological processes such as cell development and metabolic regulation. And, it is considered to be an important drug target for the treatment of cancer and metabolic diseases.
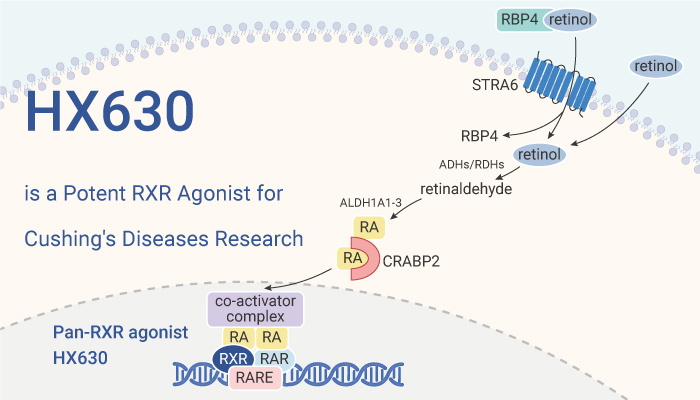
HX630 is a potent RXR agonist for Cushing’s disease research.
HX630 is a potent retinoic acid X receptor (RXR) agonist, can induce apoptosis, has an anti-tumor effect, and can be used in Cushing’s disease research. In vitro, HX630 (0.1-10 μM, 96 h) can dose-dependently inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in AtT20 cells. Firstly, it significantly inhibited AtT20 cell proliferation at 10 μM. Secondly, it decreased Pomc mRNA expression and ACTH secretion in a dose-dependent manner.
In vivo, HX630 (5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, 3 times a week for 3 weeks) reduces tumor growth in a BALB/c-nu mouse model infected with AtT20 cells. In addition, it significantly reduced tumor volume and Pomc mRNA expression in tumor cells. But body weight and plasma ACTH levels were not significantly different.
In conclusion, HX630 is a potent retinoic acid X receptor (RXR) agonist with antineoplastic effects for Cushing’s disease research.
References:
[1] Akiko Saito-Hakoda, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Dec 29;10(12):e0141960.
[2] S Minucci, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Feb;17(2):644-55.