Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a disease of progressive fibrosis and respiratory failure. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) implicates in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. ER stress activates a signaling pathway called the unfolded protein response (UPR). UPR restores homeostasis and promotes apoptosis. The bifunctional kinase/RNase IRE1α is a UPR sensor/effector that promotes apoptosis. Multiple small-molecule IRE1α inhibitors can mitigate ER stress-induced apoptosis of murine alveolar epithelial cells. Bleomycin exposure to murine lungs causes early ER stress to activate IRE1α and the terminal UPR prior to the development of pulmonary fibrosis. KIRA-7 is an imidazopyrazine compound that binds the IRE1α kinase to allosterically inhibit RNase activity.
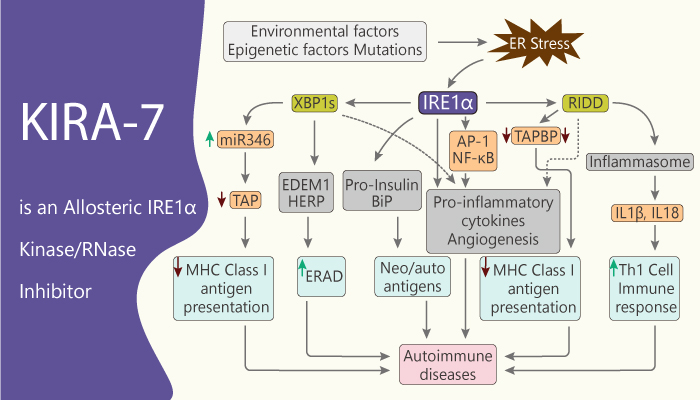
KIRA-KIRA7 provides systemically to mice at the time of Bleomycin exposure decreases terminal UPR signaling and prevents lung fibrosis. Researchers use small-molecule IRE1α kinase-inhibiting RNase attenuators (KIRAs) to evaluate the contribution of IRE1α activation to Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. To illustrate, Bleomycin (a single dose of 1.5 units/kg) induces fibrosis in mice. However, KIRA7 (5 mg/kg/day i.p.) prevents Bleomycin-induced fibrosis. Treatment of Bleomycin-exposed mice with KIRA7 results in decreased spliced XBP1 and ATF4, compared to Bleomycin exposed mice treated with vehicle. Therefore, the administration of KIRA7 14 days after Bleomycin exposure promotes the reversal of established fibrosis.
Administration of KIRA7 protects against fibrosis during the initial injury after Bleomycin, which is also when ER stress and terminal UPR markers are at their peak. Recently,
In particular, the administration of KIRA7 decreases mRNA levels of collagen and fibronectin.
In conclusion, these results demonstrate that IRE1α may be a promising target in pulmonary fibrosis and that kinase inhibitors of IRE1α may eventually be developed into efficacious anti-fibrotic drugs.