Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) belong to the endopeptidase family, which consists of 23 members. They contain zinc, are calcium dependent, and can degrade and reshape proteins to form ECM. Essentially, all members of the MMP family are associated with the development of diseases, particularly cancer metastasis, chronic inflammation, and subsequent tissue damage, as well as neurological disorders. Furthermore, dysregulation of MMP activity can lead to pathological conditions such as arthritis, inflammation, and cancer. Therefore, MMP is an important target for drug design, development, and delivery. Doxycycline is an orally active and broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor.
Doxycycline is an Orally Active MMP Inhibitor for Infection and Hypertension Research.
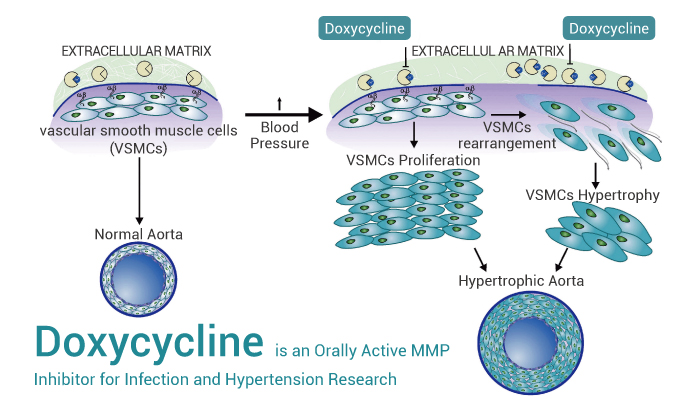
Above all, Doxycycline, an antibiotic, is an orally active and broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor. Meanwhile, Doxycycline shows antibacterial activity and anti-cancer cell proliferation activity.
Next in importance, Doxycycline with 0.01-10 µg/mL for 4 days affects growth of glioma cells only under high concentrations. Nonetheless, Doxycycline decreases MT-CO1 protein content with concentrations of 1 µg/mL and higher in SVG cells. Particularly, Doxycycline reduces proliferation of human cell lines. Doxycycline inhibits cell viability of breast cancer cells.
Once again, Doxycyclinereduces MMP-9 activity in untreated HT mice in a dose-dependent manner. Obviously, Doxycycline and Tetracycline, act systemically after absorption from the upper gastrointestinal tract. Importantly, the main advantage of Doxycycline over Tetracycline is its longer activity, and it can be taken twice or once a day.
All in all, Doxycycline is an orally active and broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor for infection and hypertension research.
References:
[1] Anna-Luisa Luger, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 17;19(5):1504.
[2] Wilfried Briest, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jun;337(3):621-7.